h76
Baron Herminius LXXVI
- Joined
- Nov 2, 2020
- Posts
- 492
- Reputation
- 840
Prologue
Hair loss is a brutal reality for men. Androgenic alopecia, the miniaturization of hair follicles caused by androgen receptor binding molecules, primarily effecting young men aged 20-29 (22.73%). Hair is an extremely vital component to your looks, which can single handedly make or break your aesthetics. Thankfully clinical pharmacology used to treat hair loss is incredibly expansive. There are a hundreds of treatments, many of which are cope. However, we fortunately have clinically proven treatments to mitigate hair loss. Today we will discuss each major treatment, what works & what should be left on the shelf.
Hair growth cycle
Anagen
Telogen
5α-Reductase Inhibitors
5α-reductase (5αr), an enzyme that converts the androgen & sex hormone testosterone into
dihydrotestosterone (DHT). While much of it is deactivated by 3α-hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase & converted into 3α-androstanediol, DHT can still bind to the androgen
receptors in the scalp which can lead to hair follicle miniaturization. This process involves shrinking the
hair follicle resulting in shorter, finer strands called vellus hair. Eventually, the hair completely
sheds & you’re left bald. Testosterone also binds to androgen receptors in your scalp, but
to a lesser extent than DHT which is ~10x more androgenic in its active form.
We can mitigate this process by taking 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride &
dutasteride. This will systematically lower serum DHT in the bloodstream, potentially leading to
side effects, which affect a small percentage of men. Finasteride & dutasteride actually have
virtually the same side effect profile [1].
Overall, 5α-reductase inhibitors are the first line of defense for hair loss. Any proper hair loss
protocol needs to include them to be effective. These compounds should NOT be taken during
development, as DHT is an essential hormone for the development of men. Since women have
low serum DHT levels biologically, these compounds will have virtually no effect on female
androgenic alopecia.
Oral Finasteride
This medication is typically prescribed in 1mg tablets for hair loss, & 5mg tablets to treat
benign prostatic hyperplasia [2]. The 1mg tablet is usually very effective for treating
androgenic alopecia. It leads to an average of ~70% serum reduction of DHT. This only blocks
type 1 5α-reductase, so it has no effect on skin & sebaceous glands. The 1mg vs. 5mg side
effect profiles are drastically different. 5mg tablet has a much higher rate of side effects,
without being more effective for treating hair loss.
Oral Dutasteride
Typically prescribed in 0.5mg tablets, however 0.5mg blocks just around 70% of DHT that is why a dose
of 2.5mg is much more optimal to treat hairloss. This blocks both type 1 & type 2 5α-reductase. It leads to
an average of roughly 95% serum reduction in DHT. While blocking more DHT, this does not lead to a clinically
significant increase in adverse effects. Many people praise oral dutasteride for its skin benefits, but this won’t
be as dramatic as something like topical retinoids. In a head-to-head trial comparing oral dutasteride to
finasteride, dutasteride wins by a long shot. However, oral dutasteride can be harder to source, & clinicians
typically prescribe finasteride over dutasteride due to a lack of understanding of both the safety & side effect
profile between the two.
Topical Compounds
Topical hair growth compounds focus on stimulating follicles and blocking DHT, usually acting
as artificial ways to ultimately prolonging the Anagen stage.
Fluocinoline
A mild corticosteroid that helps reduce inflammation & irritation in the scalp. This is mainly
used clinically to treat alopecia areata, but has a use case with androgenic alopecia as well.
Fluocinoline can ease the absorption of other topical agents, but probably won’t function very
strongly on its own. If your immune system is essentially attacking your own hair follicles,
corticosteroids can reduce the action of white blood cells in your scalp, freeing up hair follicles
to grow and prevent damage.
RU-58841
A topical anti-androgen that inhibits testosterone and DHT from binding to androgen
receptors in the scalp, with a minimal serum decrease in androgen receptor signaling.
Since testosterone also has a chance to miniaturize hair follicles in the scalp, RU can
become a good option to address androgenic alopecia. This compound is highly preferential
to AAS users, due to the fact that it promotes local androgen blockade without systemic
effects. It does not lower serum testosterone, estradiol, or DHT. Many AAS act directly
on the AR, bypassing 5αr & causing 5αris to fail. RU-58841 has compatibility with
the presence of supraphysiological androgen levels, especially with DHT derivatives
like masteron.
PTD-DBM
PTD-DBM, standing for Protein Transduction Domain-fused Dishevelled Binding Motif
is a peptide which inhibits the binding of CXXC5 to Dishevelled. This activates the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway which results in new hair growth. This supports follicular differentiation
and proliferation. Targeting CXXC5 has been proven to increase hair growth and neogenesis
KX-826
Also known as Pyrilumatide, which is a drug developed by Kintor Pharmaceuticals. Instead of
lowering DHT levels like finasteride, KX-826 directly blocks it from binding to androgen receptors
in the hair follicles ultimately preventing the hormones miniaturizing effect. It can be used as an
alternative to finasturide or minoxidil due to clinical trials suggesting minimal systemic side effects.
PP405 Ligands ~ The ultimate solution
PP405 is a compound that acts as a mitochondrial pyruvate carrier inhibitor, used topically as
a gel. This is an extremely effective & scientifically backed treatment for androgenic alopecia.
It works by stimulating lactate dehydrogenase in hair follicle stem cells, which regulates the hair
growth cycle & promotes cellular energy for hair growth. Normally, in the case of androgenic
alopecia, hair follicles tend to permanently stay in the exogen phase, catastrophizing their ability
to grow. By acting on hair follicle stem cells, PP405 reactivates hair follicles by promoting their
metabolism. Fortunately, this compound is unstable in blood serum, making the risk of systemic
absorption minimal. The chemical structure, for the most part, is unknown. The patent is owned
by Pelage Pharmaceuticals, but reverse engineering of patents has been underway for quite
some time. There are hints this will be released on everychem.com. This will be present in two
ligands of PP405: PP30 and 3HP. 3HP is the primary activator. This modulates redox
(oxidative/antioxidative) signaling within the hair follicle. This theoretically shifts the hair follicle
directly into the anagen phase. This is what actively acts on dormant hair follicles. PP30 can
act as a buffer for the oxidative stress caused by the activation of hair follicle stem cells. This
delays the transition from anagen to catagen preventing early shutdown. This doesn’t restart
the hair growth itself, but modulates the metabolism of hair follicles so they stay in the growth
phase. Together, PP30 and 3HP act as a non-androgenic growth signaling combination.
@Sadist @Nexom @Nutsack2000 @Mogs Me @adeeyeah @Orka @iblamexyz @BigBallsLarry @Cinnamon fan64 @knightgtb65 @dnrwarrior11 @Idontknow- @Laqi @nestivv @Volksstaffel @GonorrhoeaGobbler
Hair loss is a brutal reality for men. Androgenic alopecia, the miniaturization of hair follicles caused by androgen receptor binding molecules, primarily effecting young men aged 20-29 (22.73%). Hair is an extremely vital component to your looks, which can single handedly make or break your aesthetics. Thankfully clinical pharmacology used to treat hair loss is incredibly expansive. There are a hundreds of treatments, many of which are cope. However, we fortunately have clinically proven treatments to mitigate hair loss. Today we will discuss each major treatment, what works & what should be left on the shelf.
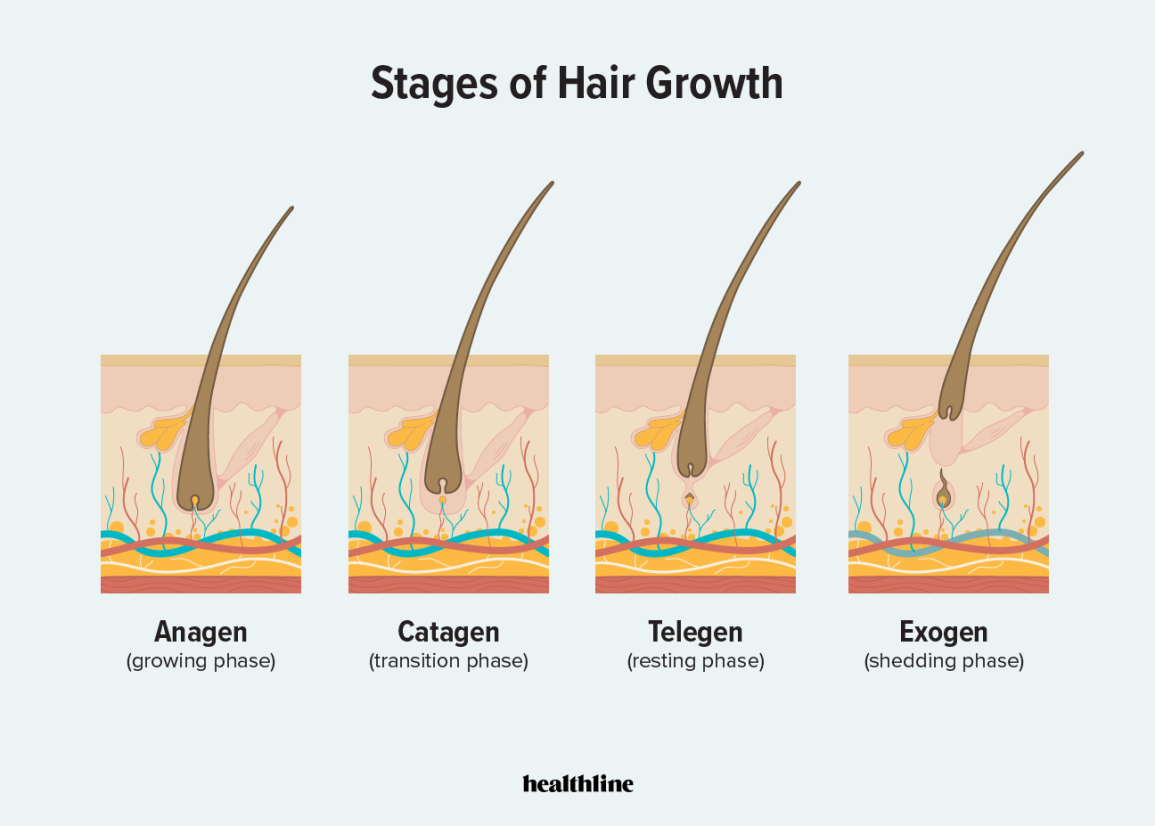
Hair growth cycle
Anagen
This is the longest phase, which lasts between 2 to 8 years. These hairs are pushed out by the
hair follicle and continue to grow until they’re cut. Representing about 85-90% of your hair. This
phase can theoretically be promoted by CXXC5 inhibitors, as discussed later.
CatagenThis phase which lasts for 2 weeks, represents about 1-3% of your hair. During this phase,
growth slows & hair follicles start to shrink. This hair separates from the hair follicle, but
doesn’t fall out.
Telogen
This phase lasts roughly 2-3 months. It represents roughly 9% of your hair. Hair wont grow
during this phase. New hair starts to form in the follicles during this phase
ExogenHair is shed from the scalp, leading to a loss of 50-100 hairs per day. This can last several
months, & during this time new hair follicles form to take their place.

5α-Reductase Inhibitors
5α-reductase (5αr), an enzyme that converts the androgen & sex hormone testosterone into
dihydrotestosterone (DHT). While much of it is deactivated by 3α-hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase & converted into 3α-androstanediol, DHT can still bind to the androgen
receptors in the scalp which can lead to hair follicle miniaturization. This process involves shrinking the
hair follicle resulting in shorter, finer strands called vellus hair. Eventually, the hair completely
sheds & you’re left bald. Testosterone also binds to androgen receptors in your scalp, but
to a lesser extent than DHT which is ~10x more androgenic in its active form.
We can mitigate this process by taking 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride &
dutasteride. This will systematically lower serum DHT in the bloodstream, potentially leading to
side effects, which affect a small percentage of men. Finasteride & dutasteride actually have
virtually the same side effect profile [1].
Overall, 5α-reductase inhibitors are the first line of defense for hair loss. Any proper hair loss
protocol needs to include them to be effective. These compounds should NOT be taken during
development, as DHT is an essential hormone for the development of men. Since women have
low serum DHT levels biologically, these compounds will have virtually no effect on female
androgenic alopecia.
Oral Finasteride
This medication is typically prescribed in 1mg tablets for hair loss, & 5mg tablets to treat
benign prostatic hyperplasia [2]. The 1mg tablet is usually very effective for treating
androgenic alopecia. It leads to an average of ~70% serum reduction of DHT. This only blocks
type 1 5α-reductase, so it has no effect on skin & sebaceous glands. The 1mg vs. 5mg side
effect profiles are drastically different. 5mg tablet has a much higher rate of side effects,
without being more effective for treating hair loss.
Oral Dutasteride
Typically prescribed in 0.5mg tablets, however 0.5mg blocks just around 70% of DHT that is why a dose
of 2.5mg is much more optimal to treat hairloss. This blocks both type 1 & type 2 5α-reductase. It leads to
an average of roughly 95% serum reduction in DHT. While blocking more DHT, this does not lead to a clinically
significant increase in adverse effects. Many people praise oral dutasteride for its skin benefits, but this won’t
be as dramatic as something like topical retinoids. In a head-to-head trial comparing oral dutasteride to
finasteride, dutasteride wins by a long shot. However, oral dutasteride can be harder to source, & clinicians
typically prescribe finasteride over dutasteride due to a lack of understanding of both the safety & side effect
profile between the two.
Topical Compounds
Topical hair growth compounds focus on stimulating follicles and blocking DHT, usually acting
as artificial ways to ultimately prolonging the Anagen stage.
Fluocinoline
A mild corticosteroid that helps reduce inflammation & irritation in the scalp. This is mainly
used clinically to treat alopecia areata, but has a use case with androgenic alopecia as well.
Fluocinoline can ease the absorption of other topical agents, but probably won’t function very
strongly on its own. If your immune system is essentially attacking your own hair follicles,
corticosteroids can reduce the action of white blood cells in your scalp, freeing up hair follicles
to grow and prevent damage.
RU-58841
A topical anti-androgen that inhibits testosterone and DHT from binding to androgen
receptors in the scalp, with a minimal serum decrease in androgen receptor signaling.
Since testosterone also has a chance to miniaturize hair follicles in the scalp, RU can
become a good option to address androgenic alopecia. This compound is highly preferential
to AAS users, due to the fact that it promotes local androgen blockade without systemic
effects. It does not lower serum testosterone, estradiol, or DHT. Many AAS act directly
on the AR, bypassing 5αr & causing 5αris to fail. RU-58841 has compatibility with
the presence of supraphysiological androgen levels, especially with DHT derivatives
like masteron.
PTD-DBM
PTD-DBM, standing for Protein Transduction Domain-fused Dishevelled Binding Motif
is a peptide which inhibits the binding of CXXC5 to Dishevelled. This activates the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway which results in new hair growth. This supports follicular differentiation
and proliferation. Targeting CXXC5 has been proven to increase hair growth and neogenesis
KX-826
Also known as Pyrilumatide, which is a drug developed by Kintor Pharmaceuticals. Instead of
lowering DHT levels like finasteride, KX-826 directly blocks it from binding to androgen receptors
in the hair follicles ultimately preventing the hormones miniaturizing effect. It can be used as an
alternative to finasturide or minoxidil due to clinical trials suggesting minimal systemic side effects.
PP405 Ligands ~ The ultimate solution
PP405 is a compound that acts as a mitochondrial pyruvate carrier inhibitor, used topically as
a gel. This is an extremely effective & scientifically backed treatment for androgenic alopecia.
It works by stimulating lactate dehydrogenase in hair follicle stem cells, which regulates the hair
growth cycle & promotes cellular energy for hair growth. Normally, in the case of androgenic
alopecia, hair follicles tend to permanently stay in the exogen phase, catastrophizing their ability
to grow. By acting on hair follicle stem cells, PP405 reactivates hair follicles by promoting their
metabolism. Fortunately, this compound is unstable in blood serum, making the risk of systemic
absorption minimal. The chemical structure, for the most part, is unknown. The patent is owned
by Pelage Pharmaceuticals, but reverse engineering of patents has been underway for quite
some time. There are hints this will be released on everychem.com. This will be present in two
ligands of PP405: PP30 and 3HP. 3HP is the primary activator. This modulates redox
(oxidative/antioxidative) signaling within the hair follicle. This theoretically shifts the hair follicle
directly into the anagen phase. This is what actively acts on dormant hair follicles. PP30 can
act as a buffer for the oxidative stress caused by the activation of hair follicle stem cells. This
delays the transition from anagen to catagen preventing early shutdown. This doesn’t restart
the hair growth itself, but modulates the metabolism of hair follicles so they stay in the growth
phase. Together, PP30 and 3HP act as a non-androgenic growth signaling combination.
@Sadist @Nexom @Nutsack2000 @Mogs Me @adeeyeah @Orka @iblamexyz @BigBallsLarry @Cinnamon fan64 @knightgtb65 @dnrwarrior11 @Idontknow- @Laqi @nestivv @Volksstaffel @GonorrhoeaGobbler
Last edited:



