MisterMercedes
Kraken
- Joined
- Jul 4, 2020
- Posts
- 3,661
- Reputation
- 3,887
One of the most dimorphic bones of the skull, there are many differences between the male and female mandible.
1) Ramus
- Length
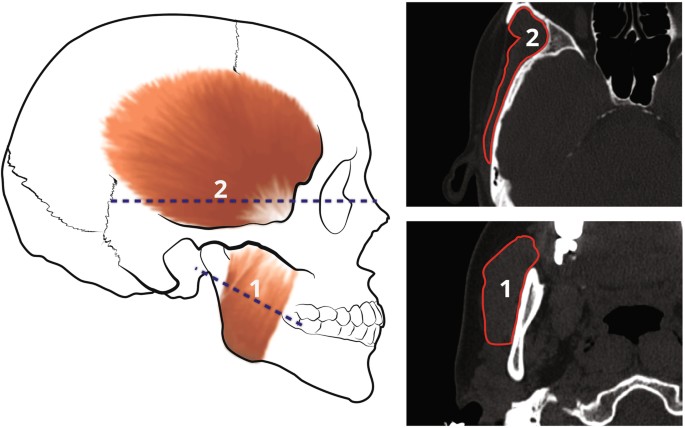
The male ramus is longer in the descending direction. This is most likely due to the greater bite force that a longer ramus yields (due to longer masseter).
Long vs short descending ramus:


The male ramus is also longer in the ascending direction. This again leads to greater bite force, but also higher cheekbones as the zygomatic process of temporal is positioned higher when the ascending ramus grows higher, and thus the cheekbones themselves are positioned higher. This leads to smaller eye sockets and is a key component of “hunter eyes”.
Long vs short ascending ramus:


Skull view of differing ramus lengths:

- Width
The male ramus is also wider than the female’s. This is partially due to greater posterior remodeling of the ramus, or, in other words, a straighter ramus that makes the jaw look more square. A straighter ramus also yields greater bite force (due to wider masseter).
Straight vs sloped ramus:


Differing ramus slopes:

In addition to greater posterior remodeling, male mandibles have larger coronoid processes. This is due to longer zygomatic processes of temporal or more forward positioned zygomatic bones. This again leads to a wider masseter and thus greater bite force.
Small vs large coronoid process:

Real life examples of males with large vs small coronoid processes:


2) Gonions
- Bigonial width
Males have wider bigonions due to greater horizontal remodelling of the ramus during development. This is related to a greater bite force, possibly due to the straighter angulation of the masseter, and also gives the mandible and teeth better protection.
Wide vs narrower bigonion:



-Gonial angulation
The gonion, where the masseter muscle attaches, evertoutwards in the male skull, whereas, in the female skull, it is straight or even inverts toward the body of the mandible. Gonial eversion is another trait associated with higher bite force.
Gonial eversion vs inversion:


To avoid the accusation of cherry picking pictures:

Skull view:

3) Symphysis (Chin)
The male chin is longer, wider, and more protrusive (due to a longer mandible overall) than the female’s.
Long vs short chin:


Wide vs narrow chin:


Long vs short mandible:


Potential dimorphic aspects of mandible:
Antegonial notch: male dimorphic trait
Posterior ramus flexure: male dimorphic trait
Sources:
1) Bite force-
 www.nature.com
www.nature.com
2) Ramus length-

 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
3) Ramus width-

 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
4) Gonions-

 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
5) Symphsis-

 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
1) Ramus
- Length
The male ramus is longer in the descending direction. This is most likely due to the greater bite force that a longer ramus yields (due to longer masseter).
Long vs short descending ramus:
The male ramus is also longer in the ascending direction. This again leads to greater bite force, but also higher cheekbones as the zygomatic process of temporal is positioned higher when the ascending ramus grows higher, and thus the cheekbones themselves are positioned higher. This leads to smaller eye sockets and is a key component of “hunter eyes”.
Long vs short ascending ramus:
Skull view of differing ramus lengths:
- Width
The male ramus is also wider than the female’s. This is partially due to greater posterior remodeling of the ramus, or, in other words, a straighter ramus that makes the jaw look more square. A straighter ramus also yields greater bite force (due to wider masseter).
Straight vs sloped ramus:
Differing ramus slopes:
In addition to greater posterior remodeling, male mandibles have larger coronoid processes. This is due to longer zygomatic processes of temporal or more forward positioned zygomatic bones. This again leads to a wider masseter and thus greater bite force.
Small vs large coronoid process:
Real life examples of males with large vs small coronoid processes:
2) Gonions
- Bigonial width
Males have wider bigonions due to greater horizontal remodelling of the ramus during development. This is related to a greater bite force, possibly due to the straighter angulation of the masseter, and also gives the mandible and teeth better protection.
Wide vs narrower bigonion:
-Gonial angulation
The gonion, where the masseter muscle attaches, evertoutwards in the male skull, whereas, in the female skull, it is straight or even inverts toward the body of the mandible. Gonial eversion is another trait associated with higher bite force.
Gonial eversion vs inversion:
To avoid the accusation of cherry picking pictures:
Skull view:
3) Symphysis (Chin)
The male chin is longer, wider, and more protrusive (due to a longer mandible overall) than the female’s.
Long vs short chin:
Wide vs narrow chin:
Long vs short mandible:
Potential dimorphic aspects of mandible:
Antegonial notch: male dimorphic trait
Posterior ramus flexure: male dimorphic trait
Sources:
1) Bite force-

Human mandibular shape is associated with masticatory muscle force - Scientific Reports
Understanding how and to what extent forces applied to the mandible by the masticatory muscles influence its form, is of considerable importance from clinical, anthropological and evolutionary perspectives. This study investigates these questions. Head CT scans of 382 adults were utilized to...
2) Ramus length-

Age and gender correlation of gonial angle, ramus height and bigonial width in dentate subjects in a dental school in Far North Queensland
This study aimed to determine if mandibular parameters (gonial angle, bigonial width and ramus height) measured from panoramic radiographs, can be used to determine a correlation with an individual’s age and gender in dentate subjects in Far North ...
3) Ramus width-

Mandibular ramus: An indicator for sex determination - A digital radiographic study
The identification of skeletal remains is of paramount importance in medico-legal investigations. The skeletal components most often investigated for gender determination are the pelvis and skull, with the mandible being a practical element to analyze ...
4) Gonions-

Sex Determination of Human Mandible Using Metrical Parameters
Introduction: Determination of sex from an unknown human bone is an important role in forensic and anthropology field. The mandible is the largest and hardest facial bone, that commonly resist post mortem damage and forms an important source of information ...

Mandibular ramus flexure and gonial eversion as morphologic indicators of sex - PubMed
Recently, two mandibular traits--ramus flexure and gonial eversion--have come under close scrutiny (Loth & Henneberg 1996, 2000). The present study investigates the reliability of these two traits when each is applied as a single and independent indicator of sex, including the question of repeat …
5) Symphsis-

Sex Determination of Human Mandible Using Metrical Parameters
Introduction: Determination of sex from an unknown human bone is an important role in forensic and anthropology field. The mandible is the largest and hardest facial bone, that commonly resist post mortem damage and forms an important source of information ...


