garoupilled_
Message me if you need help regarding your looks
- Joined
- Sep 5, 2022
- Posts
- 1,911
- Reputation
- 4,284
I just unraveled a brand new iqmaxxing method hidden in various codexes on the monasteries of Tibet (links down below) which big pharma and western medicine conglomerates DON'T want you to know about since they've recently been translated to modern English using advanced AI language softwares.
This technique has been shown across multiple ancient asian cultures to increase your intelligence quotient by an astounding margin of up to 25%
You heard it right, just by doing this one simple trick that farmaceutical companies do not want you aware of, your IQ may go from 130 to even 160, naturally.
The technique itself is based upon the premise of neurogenesis - the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells, so-called NPCs
NPCs are composed of 3 main stages and have major importance in their given role for the arrangement to come into action
Proliferation: During this stage, neural stem cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various types of cells in the nervous system, multiply through cell division. These cells can either continue dividing to produce more stem cells or differentiate into neural progenitor cells.
Differentiation: Neural progenitor cells, also known as neural precursor cells, are more specialized than neural stem cells but still have the potential to develop into different cell types, including neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. During differentiation, these cells receive specific molecular signals that guide them toward becoming a particular type of cell.
Migration and Integration: Once the cells have differentiated into neurons, they migrate to their final destination in the brain. This movement is guided by various chemical signals and physical structures in the brain. Upon reaching their destination, the new neurons integrate into the existing neural network by forming connections, called synapses, with other neurons.
The key to increasing your IQ through this process of neurogenesis was a secret to western medicine for all dawn of mankind (or maybe they're hiding it from public knowledge), nonetheless, it has now been revealed through the translation of these papers and has been broken down in a few easy steps.
To forfeit in this process is a rather difficult task given its plain framework: for which I coined it as "Brainsmashing".
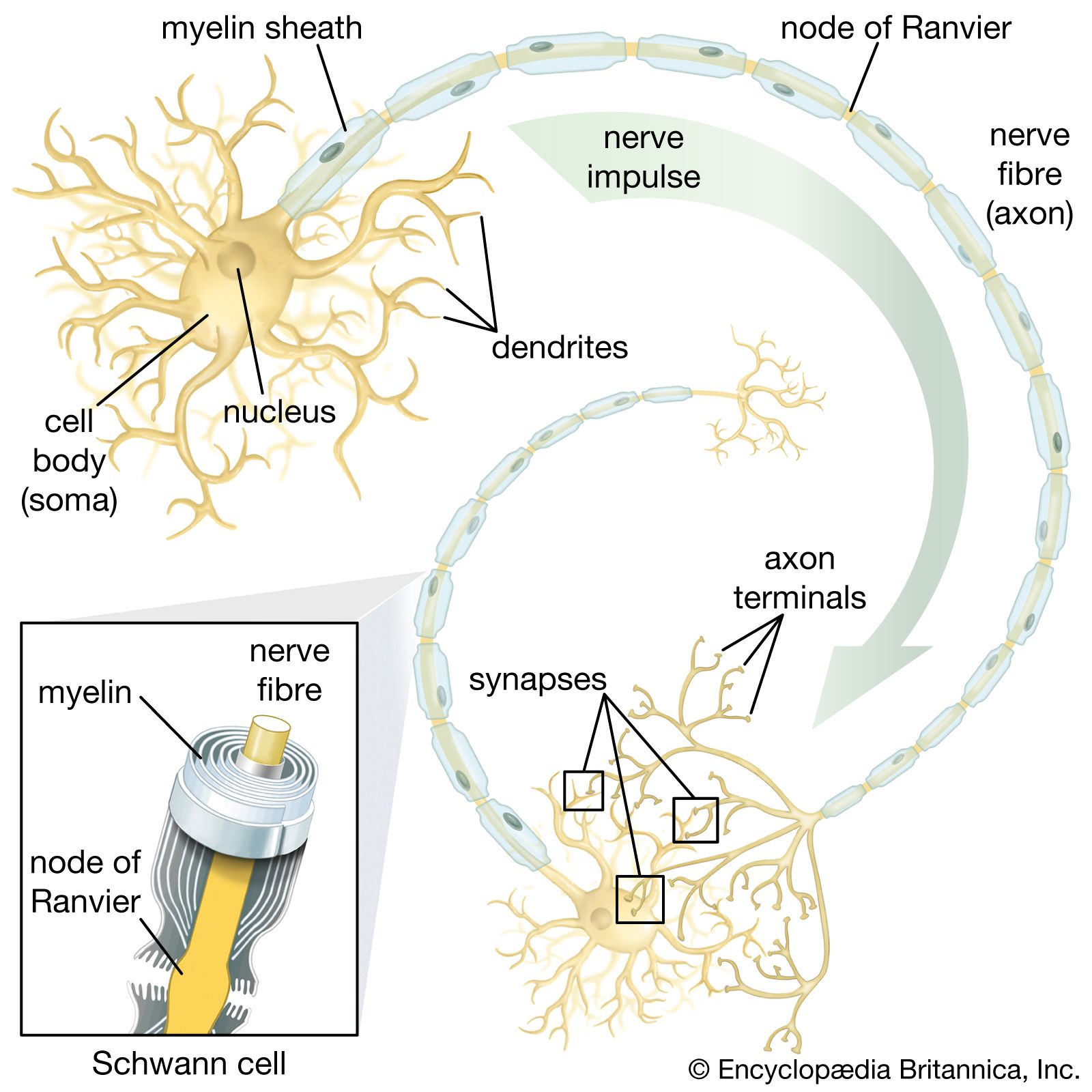
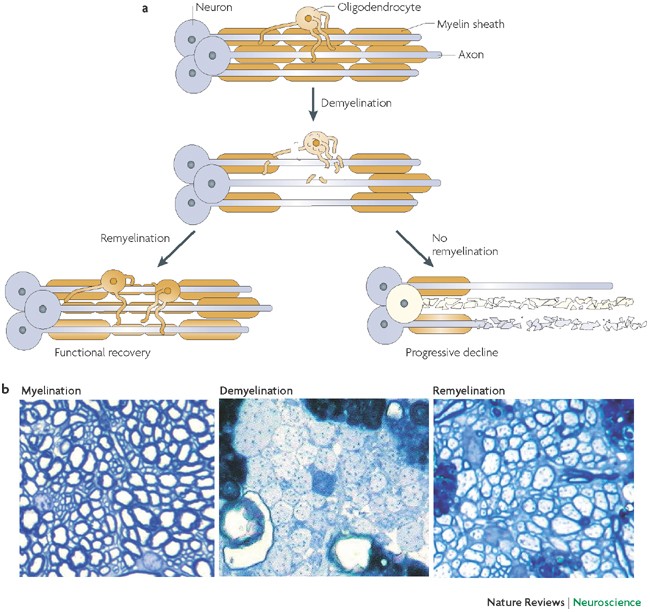
Brainsmashing, or as the Tibetean called it in their manuscripts, ཀླད་པ་དཀྲུག་དཀྲུག་བྱེད་པ།, consists of the dull act of bashing your head against hard surfaces in order to create microincisions in the myelin sheath portion of the neuron cell. By doing this, the nodes of ranvier area of the neuron, which are rich in ion channels and necessary for the generation and propagation of action potentials through influx of sodium ions, initiate a reaction chamber through various axon nodes which further causes remyelination - involved in the repair and reformation of the myelin sheath through microincisioned areas by the schwann cells and oligodendrocytes, the glial cells responsible for its production. By this first cascade response, the glial cells responsible for myelination become activated - then, both are recruited to the site of the myelin damage. These cells have the potential to differentiate into mature oligodendrocytes capable of producing new myelin. Once at the site of injury, cells undergo differentiation and proliferation to produce mature myelinating cells. Afterward, the mature glial cells wrap their cell membranes around the damaged axons to form new myelin sheaths. This new myelin sheath is wider and has longer internodal lengths (the distance between nodes of ranvier) compared to the original myelin sheath. With the formation of the new myelin sheath, the conduction of nerve impulses along the axon is improved, leading to the betterment of function. However, the extent of improvement depends on the efficiency of remyelination and other factors such as axonal integrity and the overall health of the neuron due to external factors played into brainsmashing

Curiously, there have been multiple studies that show support for this idea, across multiple fields of study on mammals, but none of them arrived at the full conclusion of the ancient Tibetan books.

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
 www.nature.com
www.nature.com

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Links to the books:
 tibetanlibrary.org
tibetanlibrary.org
 tibetanlibrary.org
tibetanlibrary.org
External factors that lead to greater brainsmashing results are varied and too much to list only in this guide, but here are a few:
1: Nutrition
The myelin sheath is composed mainly of lipids and proteins, with lipids making up about 70-80% of the dry weight and proteins making up the remaining 20-30%.
Its composition is unique, with a high proportion of glycolipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol. Some of the key lipids found in myelin include:
Galactocerebrosides: Most abundant glycolipid in the myelin sheath, particularly in the central nervous system. They play a vital role in the stability and integrity of myelin.
Sulfatides: Sulfated glycolipids that contribute to the structural organization of the myelin sheath and are involved in the interaction between myelin and the axon.
Cholesterol: Essential for maintaining the compact structure of the myelin sheath, as it participates in the formation of stable lipid-protein complexes.
The protein content of the myelin sheath consists of various myelin-specific proteins that contribute to its structure, stability, and function. The major proteins differ between the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) - in the CNS, the primary myelin proteins are proteolipid protein, which makes up about 50% of the total protein content, and myelin basic protein, which accounts for about 30%. Other proteins found in the CNS myelin include myelin-associated glycoprotein, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG), and 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase (CNPase). In the PNS, the major myelin protein is myelin protein zero, which makes up more than 50% of the total protein content. Other significant proteins in PNS myelin include peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) and myelin basic protein (MPB).
In order to ensure faster recovery from microincisions, a proper diet can help achieve this goal. For this, it is important to consume:
Omega-3 fatty acids: These essential fatty acids are important components of cell membranes, including the myelin sheath, and have anti-inflammatory properties. Good sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel, sardines), walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
B vitamins, particularly vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and folic acid, play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the nervous system, including the production and maintenance of myelin. Good sources of B vitamins include whole grains, lean meats, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and legumes.
Vitamin D has been shown to play a role in nerve health and the maintenance of myelin. Good sources of vitamin D include exposure to sunlight, fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements.
Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium, can help protect the nervous system from oxidative stress and damage. Good sources of antioxidants include fruits and vegetables (e.g., berries, citrus fruits, bell peppers, and leafy greens), nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Choline is a nutrient that is essential for the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of myelin. Good sources of choline include eggs, soybeans, beef liver, chicken, fish, and dairy products.
Iron is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system and the production of myelin. Good sources of iron include red meat, poultry, fish, legumes, fortified cereals, and leafy green vegetables.
Magnesium is involved in many processes in the nervous system, including the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of myelin. Good sources of magnesium include nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables.
Zinc is involved in the proper functioning of the nervous system and is essential for the production and maintenance of myelin. Good sources of zinc include oysters, red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and whole grains.
Proper hydration is essential for overall health, including the function of the nervous system. Drinking enough water throughout the day can help support your body's ability to maintain and repair myelin.

2: Focus on neuron-dense areas of the brain


Different regions of the brain contain different densities of neurons and functionalities. In order to increase your success chances with brainsmashing, an effective way to do this would to prefer hitting on certain areas with a higher likelihood of causing the most microincisions. In the human brain, intelligence stems mostly from:
The prefrontal cortex: located in the frontal lobes, it plays a crucial role in executive functions, such as planning, decision-making, working memory, and cognitive flexibility.
Parietal lobes: These brain regions are involved in spatial reasoning, numerical cognition, and attention.
Hippocampus: Located within the temporal lobes, the hippocampus is essential for memory formation and consolidation.
Lateral prefrontal-parietal network: includes regions in the prefrontal and parietal cortices, is involved in fluid intelligence, which is the ability to solve novel problems and adapt to new situations.
Default mode network (DMN): The DMN is a large-scale brain network that includes the medial prefrontal cortex, posterior cingulate cortex, and angular gyrus, among other regions. It is thought to be involved in various aspects of cognition, including self-referential thinking, mentalizing, and integrating information from different sources.
By locating these regions in your skull and applying pressure specifically to them you may enhance their functionality to your preference, instead of brainsmashing on unproductive areas.
3: Try different vibrations for different results
The Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses a combination of magnetic fields, radio waves, and computer processing to generate detailed images of the internal structures and organs of the body. The premise of an MRI scan is based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance, which involves the interaction of atomic nuclei with magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses.
When a patient is placed inside the MRI scanner, they are surrounded by a strong magnetic field. This magnetic field aligns the hydrogen atoms (protons) in the body's water molecules along the direction of the magnetic field. The scanner then emits a short radiofrequency pulse, which temporarily tips the protons out of their equilibrium position.
As the protons return to their equilibrium position, they release energy in the form of radio waves. This process is governed by the relaxation properties of the protons, which depend on their local environment and the type of tissue they are in. Different types of tissue have unique relaxation properties, which is one of the factors that allow MRI to generate detailed images with excellent contrast resolution.
The energy released by the protons as radio waves is detected by receiver coils placed around the body part being imaged. The detected signals are then processed by a computer, to reconstruct a detailed, cross-sectional image of the internal structures and tissues within the body.
The same premise of the MRI scan can be applied to brainsmashing - as the body is struck with the electromagnetic field and responds back to the machine, when an object is struck or hit, it can vibrate and produce sound. The energy and vibration characteristics of the object depend on its material, shape, size, and the way it is struck. Therefore, by using a plethora of objects in your brainsmashing routine, you can vary your results based on the frequency backed at your nervous tissue, yielding better results.
Conclusion
I hope this guide has been informative and mind-opening. Personally, I've been doing brainsmashing for 3 weeks and have noticed great improvements in my memory and focus during classes, and plan to continue to test its limits in neural development and biohacking enhancing on the human brain.
BOTB worthy?
This technique has been shown across multiple ancient asian cultures to increase your intelligence quotient by an astounding margin of up to 25%
You heard it right, just by doing this one simple trick that farmaceutical companies do not want you aware of, your IQ may go from 130 to even 160, naturally.
The technique itself is based upon the premise of neurogenesis - the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells, so-called NPCs
NPCs are composed of 3 main stages and have major importance in their given role for the arrangement to come into action
Proliferation: During this stage, neural stem cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various types of cells in the nervous system, multiply through cell division. These cells can either continue dividing to produce more stem cells or differentiate into neural progenitor cells.
Differentiation: Neural progenitor cells, also known as neural precursor cells, are more specialized than neural stem cells but still have the potential to develop into different cell types, including neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. During differentiation, these cells receive specific molecular signals that guide them toward becoming a particular type of cell.
Migration and Integration: Once the cells have differentiated into neurons, they migrate to their final destination in the brain. This movement is guided by various chemical signals and physical structures in the brain. Upon reaching their destination, the new neurons integrate into the existing neural network by forming connections, called synapses, with other neurons.
The key to increasing your IQ through this process of neurogenesis was a secret to western medicine for all dawn of mankind (or maybe they're hiding it from public knowledge), nonetheless, it has now been revealed through the translation of these papers and has been broken down in a few easy steps.
To forfeit in this process is a rather difficult task given its plain framework: for which I coined it as "Brainsmashing".
Brainsmashing, or as the Tibetean called it in their manuscripts, ཀླད་པ་དཀྲུག་དཀྲུག་བྱེད་པ།, consists of the dull act of bashing your head against hard surfaces in order to create microincisions in the myelin sheath portion of the neuron cell. By doing this, the nodes of ranvier area of the neuron, which are rich in ion channels and necessary for the generation and propagation of action potentials through influx of sodium ions, initiate a reaction chamber through various axon nodes which further causes remyelination - involved in the repair and reformation of the myelin sheath through microincisioned areas by the schwann cells and oligodendrocytes, the glial cells responsible for its production. By this first cascade response, the glial cells responsible for myelination become activated - then, both are recruited to the site of the myelin damage. These cells have the potential to differentiate into mature oligodendrocytes capable of producing new myelin. Once at the site of injury, cells undergo differentiation and proliferation to produce mature myelinating cells. Afterward, the mature glial cells wrap their cell membranes around the damaged axons to form new myelin sheaths. This new myelin sheath is wider and has longer internodal lengths (the distance between nodes of ranvier) compared to the original myelin sheath. With the formation of the new myelin sheath, the conduction of nerve impulses along the axon is improved, leading to the betterment of function. However, the extent of improvement depends on the efficiency of remyelination and other factors such as axonal integrity and the overall health of the neuron due to external factors played into brainsmashing


Curiously, there have been multiple studies that show support for this idea, across multiple fields of study on mammals, but none of them arrived at the full conclusion of the ancient Tibetan books.

Single-cell Stereo-seq reveals induced progenitor cells involved in axolotl brain regeneration - PubMed
The molecular mechanism underlying brain regeneration in vertebrates remains elusive. We performed spatial enhanced resolution omics sequencing (Stereo-seq) to capture spatially resolved single-cell transcriptomes of axolotl telencephalon sections during development and regeneration. Annotated...

Remyelination in the CNS: from biology to therapy - Nature Reviews Neuroscience
In the CNS, remyelination of denuded axons occurs to reinstate neuronal function. Franklin and ffrench-Constant consider the cells and molecular signals that are required for remyelination and how this knowledge can be channelled towards more effective therapies for demyelinating diseases.

Overcoming remyelination failure in multiple sclerosis and other myelin disorders - PubMed
Protecting axons from degeneration represents a major unmet need in the treatment of myelin disorders and especially the currently untreatable secondary progressive stages of multiple sclerosis (MS). Several lines of evidence indicate that ensuring myelin sheaths are restored to demyelinated...

Remyelination therapy for multiple sclerosis - PubMed
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic demyelinating disease of the central nervous system characterized by infiltration of immune cells and progressive damage to myelin and axons. All therapeutics used to treat MS have been developed to target an overactive immune response, with aims to reduce...

A regenerative approach to the treatment of multiple sclerosis - PubMed
Progressive phases of multiple sclerosis are associated with inhibited differentiation of the progenitor cell population that generates the mature oligodendrocytes required for remyelination and disease remission. To identify selective inducers of oligodendrocyte differentiation, we performed an...

Demyelination and remyelination of the caudal cerebellar peduncle of adult rats following stereotaxic injections of lysolecithin, ethidium bromide, and complement/anti-galactocerebroside: a comparative study - PubMed
Experimentally induced demyelination due to the direct injection of gliotoxic agents has provided powerful models for studying the biology of remyelination. For the most part, these models have involved injection into white matter tracts of the spinal cord. However, the spinal cord has a number...
Links to the books:
Free Download Resources - Library of Tibetan Works and Archives
 tibetanlibrary.org
tibetanlibrary.org
Photographic Archive - Library of Tibetan Works and Archives
Photographic Archive The photographic archive started off as Tibetan Architecture Documentation Cent
 tibetanlibrary.org
tibetanlibrary.org
External factors that lead to greater brainsmashing results are varied and too much to list only in this guide, but here are a few:
1: Nutrition
The myelin sheath is composed mainly of lipids and proteins, with lipids making up about 70-80% of the dry weight and proteins making up the remaining 20-30%.
Its composition is unique, with a high proportion of glycolipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol. Some of the key lipids found in myelin include:
Galactocerebrosides: Most abundant glycolipid in the myelin sheath, particularly in the central nervous system. They play a vital role in the stability and integrity of myelin.
Sulfatides: Sulfated glycolipids that contribute to the structural organization of the myelin sheath and are involved in the interaction between myelin and the axon.
Cholesterol: Essential for maintaining the compact structure of the myelin sheath, as it participates in the formation of stable lipid-protein complexes.
The protein content of the myelin sheath consists of various myelin-specific proteins that contribute to its structure, stability, and function. The major proteins differ between the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) - in the CNS, the primary myelin proteins are proteolipid protein, which makes up about 50% of the total protein content, and myelin basic protein, which accounts for about 30%. Other proteins found in the CNS myelin include myelin-associated glycoprotein, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG), and 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase (CNPase). In the PNS, the major myelin protein is myelin protein zero, which makes up more than 50% of the total protein content. Other significant proteins in PNS myelin include peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) and myelin basic protein (MPB).
In order to ensure faster recovery from microincisions, a proper diet can help achieve this goal. For this, it is important to consume:
Omega-3 fatty acids: These essential fatty acids are important components of cell membranes, including the myelin sheath, and have anti-inflammatory properties. Good sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel, sardines), walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
B vitamins, particularly vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and folic acid, play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the nervous system, including the production and maintenance of myelin. Good sources of B vitamins include whole grains, lean meats, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and legumes.
Vitamin D has been shown to play a role in nerve health and the maintenance of myelin. Good sources of vitamin D include exposure to sunlight, fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements.
Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium, can help protect the nervous system from oxidative stress and damage. Good sources of antioxidants include fruits and vegetables (e.g., berries, citrus fruits, bell peppers, and leafy greens), nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Choline is a nutrient that is essential for the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of myelin. Good sources of choline include eggs, soybeans, beef liver, chicken, fish, and dairy products.
Iron is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system and the production of myelin. Good sources of iron include red meat, poultry, fish, legumes, fortified cereals, and leafy green vegetables.
Magnesium is involved in many processes in the nervous system, including the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of myelin. Good sources of magnesium include nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables.
Zinc is involved in the proper functioning of the nervous system and is essential for the production and maintenance of myelin. Good sources of zinc include oysters, red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and whole grains.
Proper hydration is essential for overall health, including the function of the nervous system. Drinking enough water throughout the day can help support your body's ability to maintain and repair myelin.
2: Focus on neuron-dense areas of the brain


Different regions of the brain contain different densities of neurons and functionalities. In order to increase your success chances with brainsmashing, an effective way to do this would to prefer hitting on certain areas with a higher likelihood of causing the most microincisions. In the human brain, intelligence stems mostly from:
The prefrontal cortex: located in the frontal lobes, it plays a crucial role in executive functions, such as planning, decision-making, working memory, and cognitive flexibility.
Parietal lobes: These brain regions are involved in spatial reasoning, numerical cognition, and attention.
Hippocampus: Located within the temporal lobes, the hippocampus is essential for memory formation and consolidation.
Lateral prefrontal-parietal network: includes regions in the prefrontal and parietal cortices, is involved in fluid intelligence, which is the ability to solve novel problems and adapt to new situations.
Default mode network (DMN): The DMN is a large-scale brain network that includes the medial prefrontal cortex, posterior cingulate cortex, and angular gyrus, among other regions. It is thought to be involved in various aspects of cognition, including self-referential thinking, mentalizing, and integrating information from different sources.
By locating these regions in your skull and applying pressure specifically to them you may enhance their functionality to your preference, instead of brainsmashing on unproductive areas.
3: Try different vibrations for different results
The Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses a combination of magnetic fields, radio waves, and computer processing to generate detailed images of the internal structures and organs of the body. The premise of an MRI scan is based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance, which involves the interaction of atomic nuclei with magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses.
When a patient is placed inside the MRI scanner, they are surrounded by a strong magnetic field. This magnetic field aligns the hydrogen atoms (protons) in the body's water molecules along the direction of the magnetic field. The scanner then emits a short radiofrequency pulse, which temporarily tips the protons out of their equilibrium position.
As the protons return to their equilibrium position, they release energy in the form of radio waves. This process is governed by the relaxation properties of the protons, which depend on their local environment and the type of tissue they are in. Different types of tissue have unique relaxation properties, which is one of the factors that allow MRI to generate detailed images with excellent contrast resolution.
The energy released by the protons as radio waves is detected by receiver coils placed around the body part being imaged. The detected signals are then processed by a computer, to reconstruct a detailed, cross-sectional image of the internal structures and tissues within the body.
The same premise of the MRI scan can be applied to brainsmashing - as the body is struck with the electromagnetic field and responds back to the machine, when an object is struck or hit, it can vibrate and produce sound. The energy and vibration characteristics of the object depend on its material, shape, size, and the way it is struck. Therefore, by using a plethora of objects in your brainsmashing routine, you can vary your results based on the frequency backed at your nervous tissue, yielding better results.
Conclusion
I hope this guide has been informative and mind-opening. Personally, I've been doing brainsmashing for 3 weeks and have noticed great improvements in my memory and focus during classes, and plan to continue to test its limits in neural development and biohacking enhancing on the human brain.
BOTB worthy?
@Curry Suicide @Patient A @House Lannister @Tallooksmaxxer @Arborist @hormonetherapy @zv1212 @Jamesothy @cloUder @curlyheadjames @Chad1212 @LiteralCaucasian @Shako Mako @Umbra @Corleone @ascension! @BrahminBoss @Beastimmung @Exterminator @seth @5.5psl @Solar @loksr @nitesik @Xangsane @khvirgin @subhuman incel @defezman @JovenCansao @Amnesia @forevergymcelling @MoggerGaston @aBetterMii @Pikabro @Dr. Bruh @Dystopian @rand anon @Alexanderr @;-; @Eduardo DOV @Tyronecell @Gargantuan @Uglybrazilian @Cauã @MatheusCqb @Beetlejuice @Bvnny. @Iasacrko @szolliontaraelis @skinnytwink @gymmaxedhorse @fnafmaxxer @MagnusTheRed @skorp @theL @PYT @ihatereddit @Brazitard @Kevin Logan @Zures @casadebanho @whiteissuperior @latino_ @Ritalincel @Tyrion! @Entschuldigung @RAITEIII @Unsh @gribsufer1 @spongebob @kumquat @KingBetaTut @Blackgymmax @JailedAristocrat @soldier_puzzle662 @Lawton88 @TRUE_CEL @2d v2 @Matthias8272 @Anstrum95 @tomsmith @Thomas DOM @Yuno_howitez @Mumbai Sissy @Hiraeth @FastBananaCEO @StepbroMo @Bashan @Prettyboy @Hades @BucketCrab @wannakms @Witheredly90 @the BULL @Vermilioncore @cvzvvc @dimorphism @SaintOverBuddyBoyo @pneumocystosis @enchanted_elixir @leveruis @Lev Peshkov @yves





