popped
Bronze
- Joined
- Jan 30, 2023
- Posts
- 473
- Reputation
- 783
We all know that swallowing the blackpill means excepting will be slutty for the right guy at the right time or mood.
The extent of female promiscuity is typically influenced by culture, but I’ll argue that biological factors such as sexual dimorphism between the genders within a group play an important role.
Species with higher sexual rates of sexual dimorphism are more polygamous and promiscuous then those with lower rates of sexual dimorphism.

 academic.oup.com
academic.oup.com
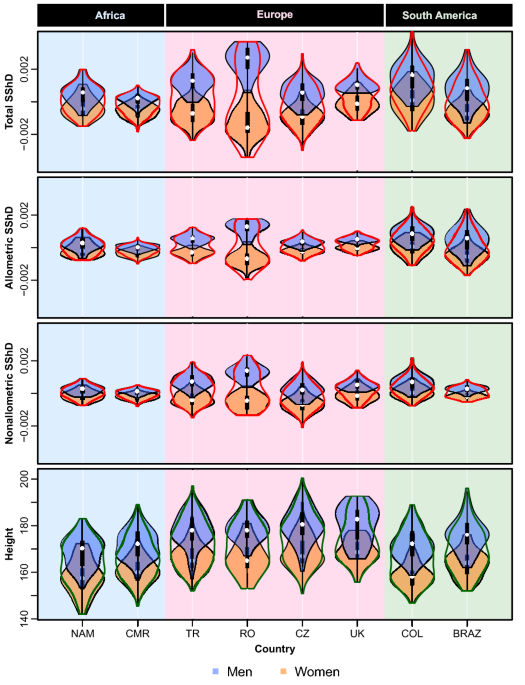
Sexual dimorphism even in humans differs by race:
 www.nature.com
www.nature.com
TL;DR
Greater sexual dimorphism in a species correlates with higher rates of male intrasexual competition, a tendency towards polygamy or polyandry and female promiscuity.
Lower rates of sexual dimorphism correlate to higher rates of monogamy, less male competition, and less promiscuity.
Among the races sexual rate of sexual dimorphism highest to lowest:
1) European
2) Hispanic
3) black
4) asian
The extent of female promiscuity is typically influenced by culture, but I’ll argue that biological factors such as sexual dimorphism between the genders within a group play an important role.
Species with higher sexual rates of sexual dimorphism are more polygamous and promiscuous then those with lower rates of sexual dimorphism.
In mammals, species with high sexual size dimorphism tend to have highly polygynous mating systems associated with high variance in male lifetime reproductive success (LRS), leading to a high opportunity for sexual selection.

Mating system, sexual dimorphism, and the opportunity for sexual selection in a territorial ungulate
Abstract. In mammals, species with high sexual size dimorphism tend to have highly polygynous mating systems associated with high variance in male lifetime
The researchers in this field agree that it is polygyny that causes sexual dimorphism in size, not the other way around. While the theory of how polygyny leads to sexual dimorphism in size has never been clearly articulated (Willner & Martin, 1985), the causal logic usually goes as follows:
(1) Relative to monogamy, polygyny creates greater fitness variance among males than among females, by allowing a few males to monopolize all females in the breeding group. Under polygyny, a few males attain great reproductive success while many remain childless, whereas almost all females reproduce more or less equally.
(2) The greater fitness variance among males increases intrasexual selective pressure among them. Under the severe physical competition for mates, only big and tall males can emerge victorious and get mating opportunities, while small and short males are left out of the reproductive opportunities altogether. At the same time, among pair-bonding species such as humans, females prefer to mate with big and tall males who can provide better physical protection for themselves and their children against predators and other males.
(3) Thus, through both intrasexual and intersexual selection, only big and tall males can reproduce and pass on their ‘big and tall male’ genes to their sons, while most or all females (of all sizes) reproduce and pass on their full range of sizes to their daughters. Over many generations, males will get bigger and taller, while females will retain the same distributions of height and weight in each generation.
Sexual body size dimorphism is correlated with intermale competition and mating system. Species with a monogamous mating system tend to show little to no dimorphism while those with high intermale competition, as occurs in in polygynous or promiscuous mating systems, exhibit greater dimorphism.
Sexual dimorphism even in humans differs by race:
In particular, European and South American populations display larger levels of facial sexual dimorphism than African populations

How and why patterns of sexual dimorphism in human faces vary across the world - Scientific Reports
Sexual selection, including mate choice and intrasexual competition, is responsible for the evolution of some of the most elaborated and sexually dimorphic traits in animals. Although there is sexual dimorphism in the shape of human faces, it is not clear whether this is similarly due to mate...
There was a negative correlation across populations between lean mass dimorphism and adiposity dimorphism, independent of temperature. With decreasing temperature, dimorphism in both lean mass and adiposity increased. Dimorphism increased in fatter but not taller populations, independently of temperature.' This means that European women are more physically different from European men than African women are from African men or than Asian women are from Asian men.
Gender was found to vary more for White faces, resulting in a negative or positive correlation between gender and race when only considering male or only considering female faces. This increased sexual dimorphism for White faces may provide an alternative explanation for differences in face processing between White and Asian faces
TL;DR
Greater sexual dimorphism in a species correlates with higher rates of male intrasexual competition, a tendency towards polygamy or polyandry and female promiscuity.
Lower rates of sexual dimorphism correlate to higher rates of monogamy, less male competition, and less promiscuity.
Among the races sexual rate of sexual dimorphism highest to lowest:
1) European
2) Hispanic
3) black
4) asian


