killuacel
Number 1 Isotretinoin Fan
- Joined
- Oct 8, 2025
- Posts
- 1,107
- Reputation
- 1,542
The 5 most important factors that contribute towards an attractive eye area
Not in order but let me know what you think the correct order is- and any other factors that as equally important.
1. Eye spacing
Refers to the distance between the eyes.
Various different measurements to determine ones eye spacing.
Intercanthal distance (ICD)
 Ideal is around 33-34mm for most males
Ideal is around 33-34mm for most males
Equally a 'one eye apart test' can be used in which the Palpebral Fissure Length of the eye fits perfectly into the intercanthal space
Interpupillary distance
 Ideal is around 65-67mm for most males
Ideal is around 65-67mm for most males
Eye spacing ratio (ESR)
 Measured by dividing the interpupillary distance by the bizygomatic width
Measured by dividing the interpupillary distance by the bizygomatic width
Ideal in males is around 44.5-47% in males- though depending on the formula there can be more or less leniency.
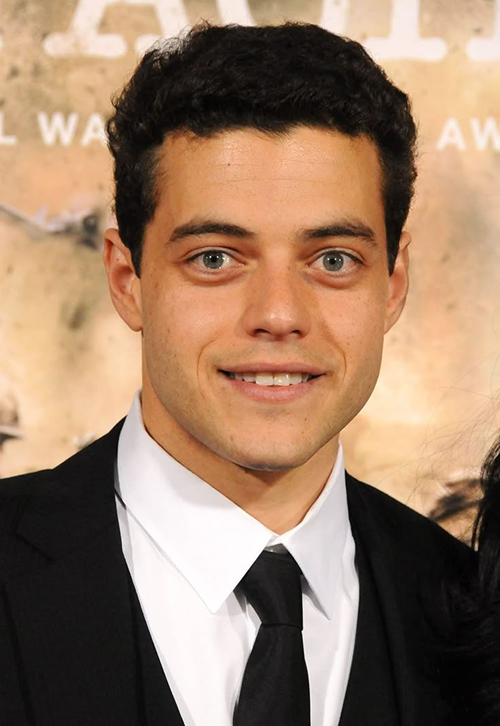
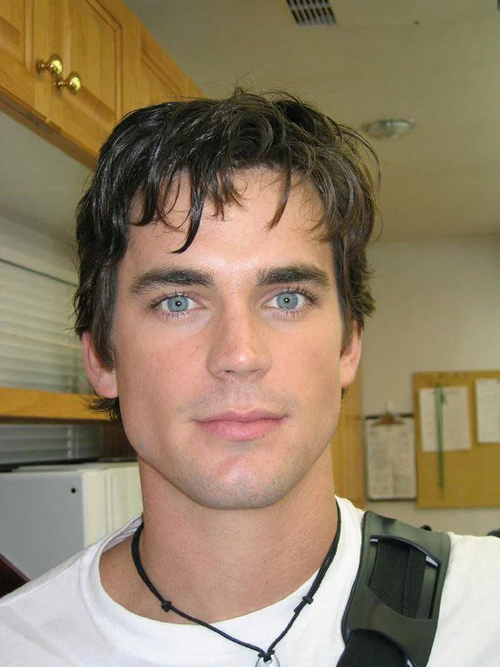
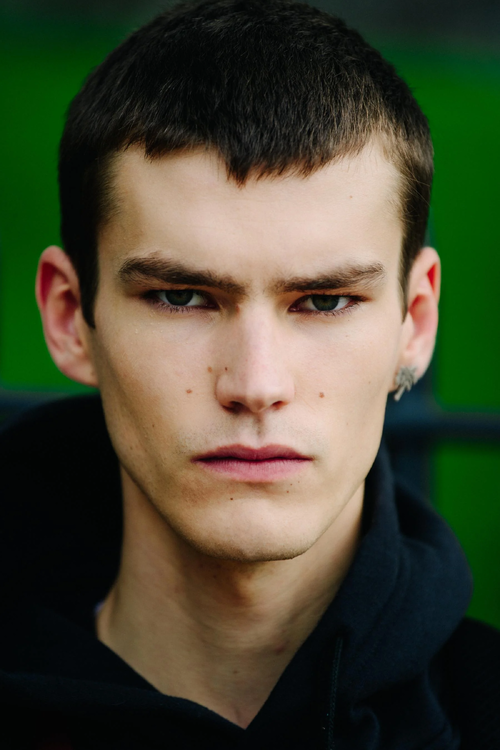
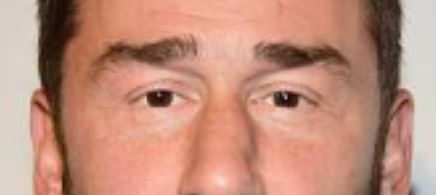
Example of poorly spaced eyes (close set)
 Example of ideally spaced eyes
Example of ideally spaced eyes
 Example of poorly spaced eyes (wide set)
Example of poorly spaced eyes (wide set)
 Research
Research
2. Eyebrows
Dark, dense and low set eyebrows are preferred in males. They contribute to a masculine and striking eye area.
In order to measure the eyebrow setness, we take the distance from the pupils to the top of the lip and divide by the lowest point of the eyebrows to the top of the lip
 Example of extremely low set eyebrows (97%)
Example of extremely low set eyebrows (97%)

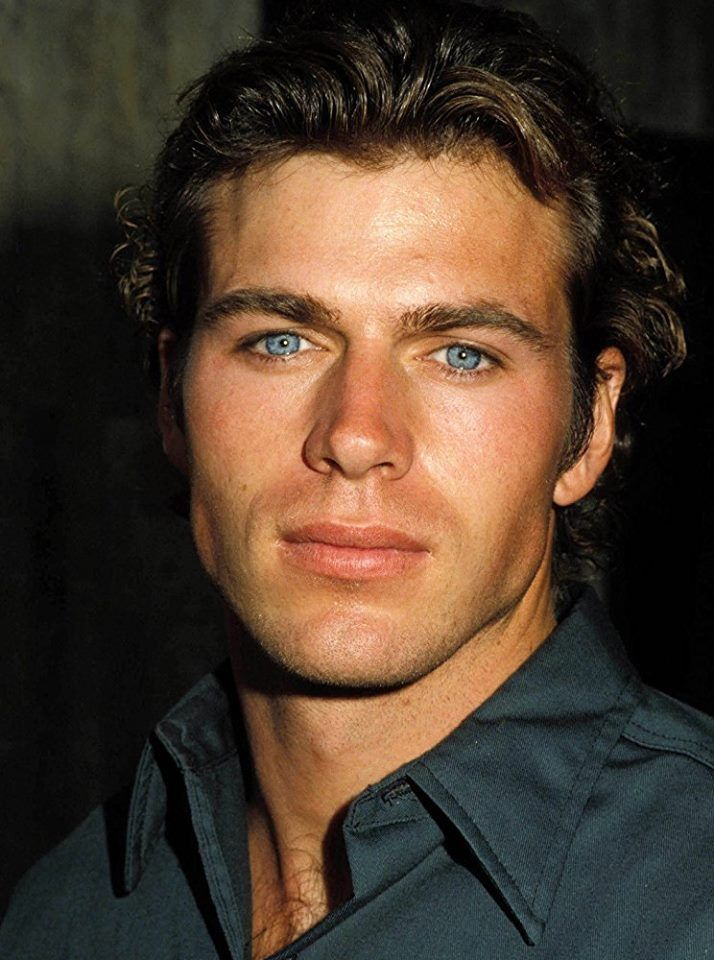
3. Supraorbital and Infraorbital development
The infraorbitals
Refers mainly to the maxilla just below the orbital rim.
A well-developed infraorbital region supports the under-eye area and upper cheek, giving a smooth lid–cheek transition.
Adequate forward projection here is associated with midface support, reduced under-eye hollowing, and a more youthful, rested appearance.
Deficiency or retrusion can visually lengthen the lower eyelid and make the midface appear flatter or more recessed.
 Example of poor infraorbitals
Example of poor infraorbitals
 Example of great infraorbitals
Example of great infraorbitals

The supraorbitals
The frontal bone above the eyes, includes the brow ridge.
Projection affects brow prominence and how deep-set the eyes appear.
Key for sexual dimorphism.
Also contributes to upper eye lid exposure.
 Example of poor supraorbitals
Example of poor supraorbitals
 Example of great supraorbitals
Example of great supraorbitals

4.Canthal tilt
Refers to the angle between the medial canthus and lateral canthus of the eye.
Positive Canthal Tilt
Gives the eyes a lifted appearance.
Makes the face look more youthful, alert, and approachable.
Creates the impression of energy and symmetry - even slight lift can make someone appear more confident or “awake.”
 Negative Canthal tilt
Negative Canthal tilt
Eyes appear droopy or downturned, sometimes giving a sad, tired, or softer expression.
Can make the upper face look heavier or less defined.
 Ideal in males-5 to 8 degrees positive
Ideal in males-5 to 8 degrees positive
Research
5. Palpebral Fissure Length/Eye aspect ratio
Palpebral fissure length refers to the horizontal distance between the inner and outer corners of the eye. It is measured from the endocanthion to the exocanthion.
The 'eye aspect ratio' divides the palpebral fissure length by the height of the eye.
 A higher eye aspect ratio contributes to a masculine, striking look. The eyes are longer and more compact- giving that 'hunter eyed' appearance.
A higher eye aspect ratio contributes to a masculine, striking look. The eyes are longer and more compact- giving that 'hunter eyed' appearance.
A lower eye aspect ratio causes a more feminine, softer look. The eyes are rounder and more 'approachable'
The eye aspect ratio is a dimorphic ratio, with men tending to have a higher EAR and females lower.
The ideal in men is around 2.8 to 3.6

 Research
Research
Hope you enjoyed reading

Not in order but let me know what you think the correct order is- and any other factors that as equally important.
1. Eye spacing
Refers to the distance between the eyes.
Various different measurements to determine ones eye spacing.
Intercanthal distance (ICD)
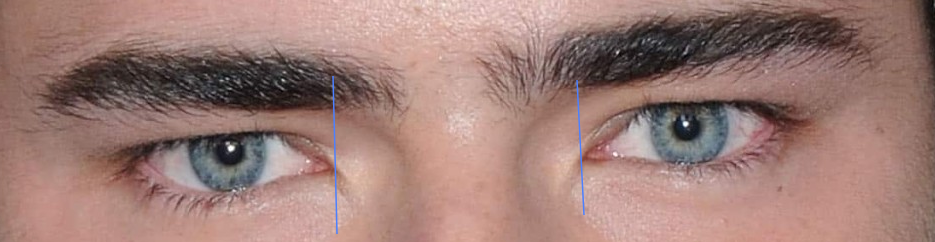
Equally a 'one eye apart test' can be used in which the Palpebral Fissure Length of the eye fits perfectly into the intercanthal space
Interpupillary distance
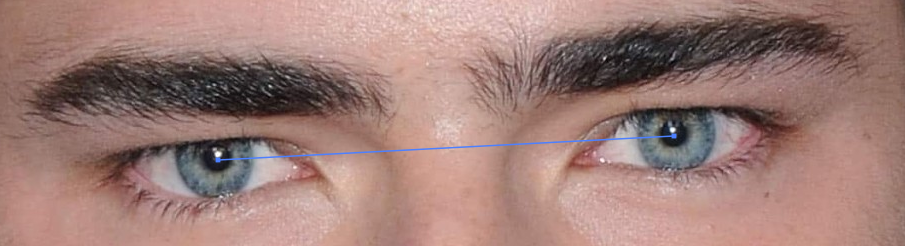
Eye spacing ratio (ESR)

Ideal in males is around 44.5-47% in males- though depending on the formula there can be more or less leniency.
Example of poorly spaced eyes (close set)

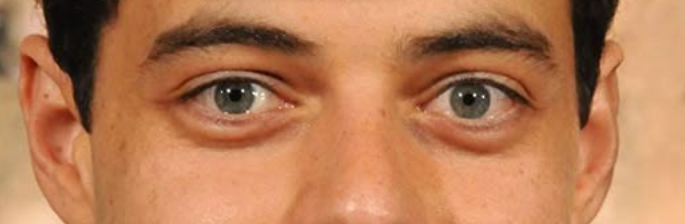
2. Eyebrows
Dark, dense and low set eyebrows are preferred in males. They contribute to a masculine and striking eye area.
In order to measure the eyebrow setness, we take the distance from the pupils to the top of the lip and divide by the lowest point of the eyebrows to the top of the lip
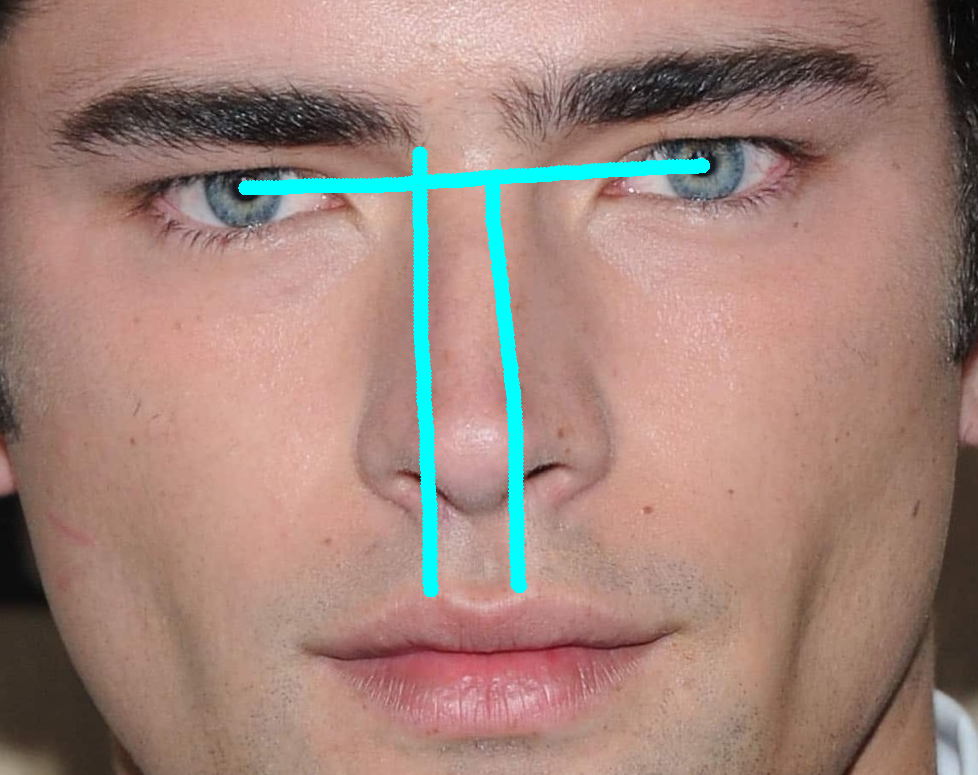

3. Supraorbital and Infraorbital development
The infraorbitals
Refers mainly to the maxilla just below the orbital rim.
A well-developed infraorbital region supports the under-eye area and upper cheek, giving a smooth lid–cheek transition.
Adequate forward projection here is associated with midface support, reduced under-eye hollowing, and a more youthful, rested appearance.
Deficiency or retrusion can visually lengthen the lower eyelid and make the midface appear flatter or more recessed.
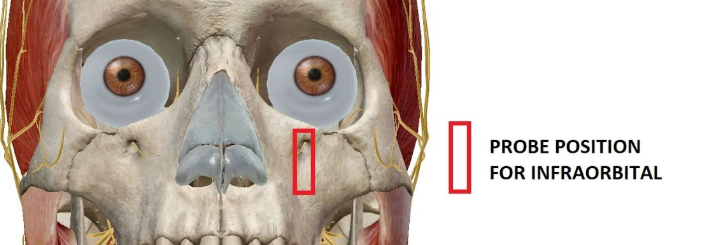
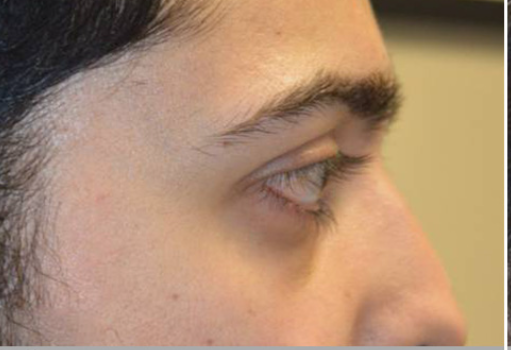

The supraorbitals
The frontal bone above the eyes, includes the brow ridge.
Projection affects brow prominence and how deep-set the eyes appear.
Key for sexual dimorphism.
Also contributes to upper eye lid exposure.
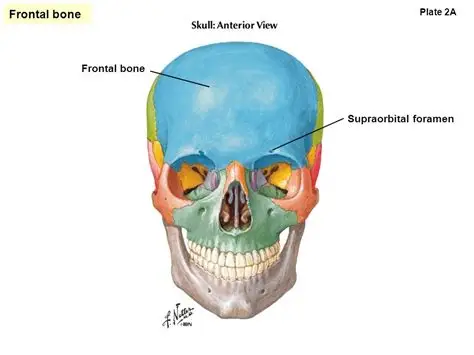
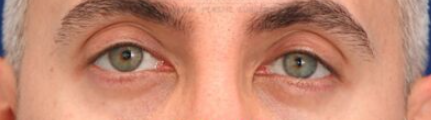

4.Canthal tilt
Refers to the angle between the medial canthus and lateral canthus of the eye.
Positive Canthal Tilt
Gives the eyes a lifted appearance.
Makes the face look more youthful, alert, and approachable.
Creates the impression of energy and symmetry - even slight lift can make someone appear more confident or “awake.”
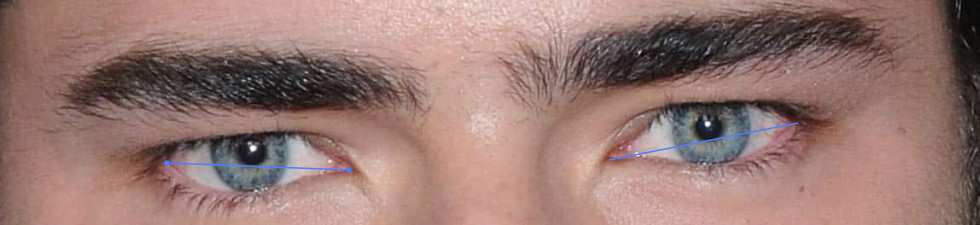
Eyes appear droopy or downturned, sometimes giving a sad, tired, or softer expression.
Can make the upper face look heavier or less defined.
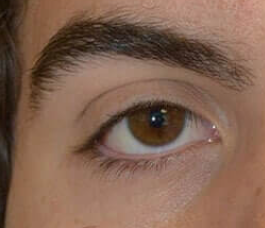
Research
5. Palpebral Fissure Length/Eye aspect ratio
Palpebral fissure length refers to the horizontal distance between the inner and outer corners of the eye. It is measured from the endocanthion to the exocanthion.
The 'eye aspect ratio' divides the palpebral fissure length by the height of the eye.
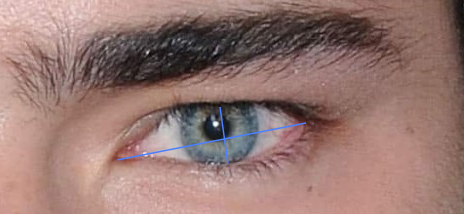
A lower eye aspect ratio causes a more feminine, softer look. The eyes are rounder and more 'approachable'
The eye aspect ratio is a dimorphic ratio, with men tending to have a higher EAR and females lower.
The ideal in men is around 2.8 to 3.6

Hope you enjoyed reading


Attachments
Last edited:







