unon
Just a neighbourhood ✨Cutie ✨
- Joined
- Apr 25, 2025
- Posts
- 2,999
- Reputation
- 6,015
AROMATASE INHIBITORS
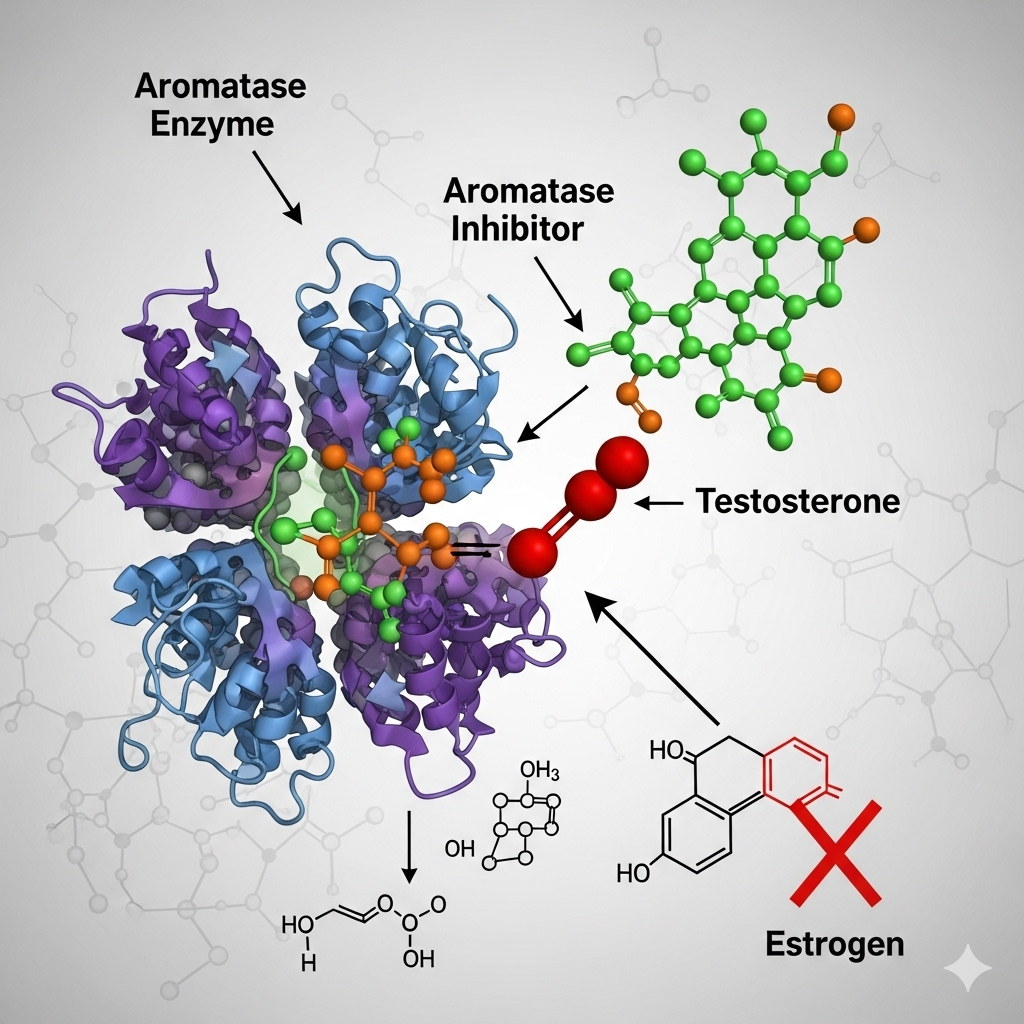
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs)
are a class of drugs that block the aromatase enzyme,
which converts androgens into estrogen.
By inhibiting this process,
AIs significantly lower estrogen levels in the body.
AROMATASE INHIBITOR USES
HEIGHT
HIGH ESTROGEN
Gynecomastia
TYPES AROMATASE INHIBITOR
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs)
are a class of drugs that block the aromatase enzyme,
which converts androgens into estrogen.
By inhibiting this process,
AIs significantly lower estrogen levels in the body.

AROMATASE INHIBITOR USES
HEIGHT
HIGH ESTROGEN
Gynecomastia
TYPES AROMATASE INHIBITOR
Anastrozole (Arimidex)
is a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor
Its mechanism involves a reversible and competitive
binding to the active site of the aromatase enzyme,
effectively blocking the conversion of androgens to estrogen
binding to the active site of the aromatase enzyme,
effectively blocking the conversion of androgens to estrogen
The drug has a long half-life of approximately 40 to 50 hours,
allowing for a convenient eod dosing regimen of 1 mg

Letrozole
is a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor.
Its mechanism is to specifically and potently block the aromatase enzyme
Dosing: The standard and recommended dose of letrozole is
2.5 mg eod
Exemestane (brand name: Aromasin)
is a steroidal aromatase inhibitor. Unlike its non-steroidal counterparts,
it works as an irreversible "suicide" inhibitor. Its structure is similar to the natural substrate,
androstenedione. It binds to the aromatase enzyme's active site and is processed
into an intermediate that permanently deactivates the enzyme.
This necessitates the creation of new enzymes to restore function.
The standard dosing is 12.5 mg taken eod after a meal
Exemestane has a mean terminal half-life of approximately 24 hours
why use aromatase inhibitors
HEIGHT
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs)
are used to increase final height by delaying the fusion of growth plates in bones.
Estrogen, even in males, is the primary hormone responsible for triggering this process,
which stops a person from growing taller. By inhibiting the aromatase enzyme,
AIs reduce the body's estrogen synthesis. This action slows down bone maturation
and prolongs the period of linear growth, ultimately leading to a potential
increase in final adult height. This therapy is primarily investigated in adolescent
boys with short stature or rapid pubertal development
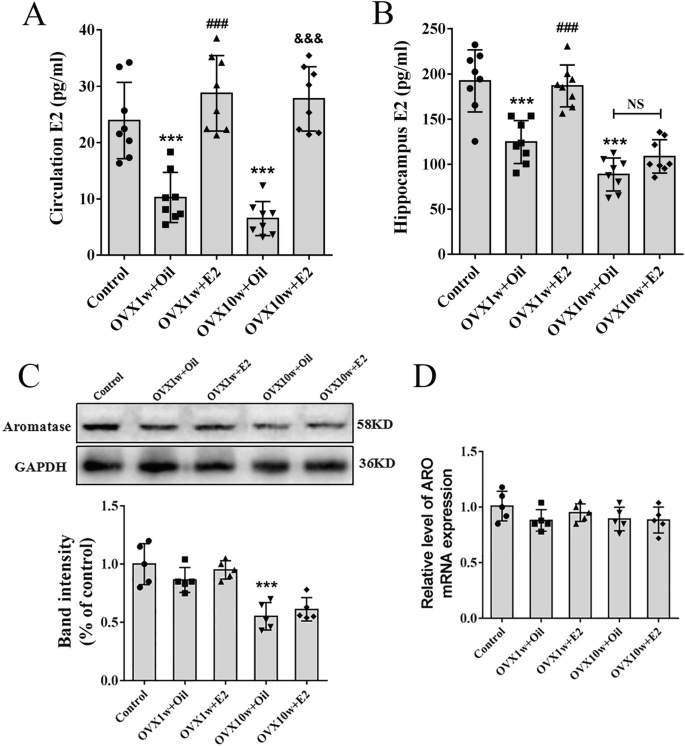
The figure above (Panel C) illustrates how ovariectomy (OVX)
can affect aromatase protein expression, with a notable reduction, particularly after 10 weeks
While this specific study is in the context of ovarian function
and estrogen levels in the hippocampus, it generally supports the principle
that aromatase activity, which AIs target, is crucial for estrogen synthesis
Aromatase inhibitors have been used in various conditions,
including gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty in boys and girls,
and in boys with familial male-limited precocious puberty
They are also explored in combination with other treatments, such as growth hormone (GH)
for conditions like idiopathic short stature (ISS) and growth hormone deficiency
instance, a network meta-analysis compared the efficacy of GH, testosterone
, and AIs in promoting height gain in children and adolescents with ISS
Another meta-analysis specifically evaluated
the effects of combined
AIs and recombinant human GH (rhGH)
versus rhGH alone for short stature,
the result showed a better result for RHGH + AI
in summery
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are used to increase height by delaying the fusion
of growth plates in bones. The hormone estrogen, present in both sexes, is responsible for this process.
By inhibiting the aromatase enzyme, AIs reduce estrogen levels, which in turn slows down bone maturation.
This prolongs the period of linear growth, potentially leading to a greater final adult height
FOR TRT
High-dose Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
is often combined with an aromatase inhibitor (AI) to manage the conversion of testosterone to estrogen.
This conversion, mediated by the aromatase enzyme, can be significant with high testosterone doses and lead
to unwanted side effects like gynecomastia, fluid retention, and mood changes.
By blocking the aromatase enzyme, AIs such as anastrozole effectively lower estradiol (a form of estrogen) levels,
thereby preventing or reducing these estrogenic side effects. This combination therapy
is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance between testosterone and estrogen.
While estrogen is vital for male health, excessively high levels are detrimental.
The use of AIs allows for a controlled reduction in estrogen, ensuring that the benefits of TRT such as improved muscle mass
, libido, and energy are achieved without the negative consequences of estrogen dominance.
HOW TO DOSE
In the context of TRT in men,
the goal of AI co-administration is typically to prevent or manage elevated E2 levels
that can arise from the aromatization of exogenous testosterone
The average serum E2 (estradiol) level in adult men generally falls within the range of 10-50 pg/mL
which should be the ideal level after AIs
NOTE I CANT GIVE YOU AN EXACT
DOSES.THE AMOUNT
YOU SHOUD TAKE DEPEND ON BLOOD WORK
In the context of height
the level should be around 10-20 pg/mL
NOTE I CANT GIVE YOU AN EXACT
DOSES.THE AMOUNT
YOU SHOUD TAKE DEPEND ON BLOOD WORK
is a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor.
Its mechanism is to specifically and potently block the aromatase enzyme
Dosing: The standard and recommended dose of letrozole is
2.5 mg eod

Exemestane (brand name: Aromasin)
is a steroidal aromatase inhibitor. Unlike its non-steroidal counterparts,
it works as an irreversible "suicide" inhibitor. Its structure is similar to the natural substrate,
androstenedione. It binds to the aromatase enzyme's active site and is processed
into an intermediate that permanently deactivates the enzyme.
This necessitates the creation of new enzymes to restore function.
The standard dosing is 12.5 mg taken eod after a meal
Exemestane has a mean terminal half-life of approximately 24 hours

why use aromatase inhibitors
HEIGHT
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs)
are used to increase final height by delaying the fusion of growth plates in bones.
Estrogen, even in males, is the primary hormone responsible for triggering this process,
which stops a person from growing taller. By inhibiting the aromatase enzyme,
AIs reduce the body's estrogen synthesis. This action slows down bone maturation
and prolongs the period of linear growth, ultimately leading to a potential
increase in final adult height. This therapy is primarily investigated in adolescent
boys with short stature or rapid pubertal development

The figure above (Panel C) illustrates how ovariectomy (OVX)
can affect aromatase protein expression, with a notable reduction, particularly after 10 weeks
While this specific study is in the context of ovarian function
and estrogen levels in the hippocampus, it generally supports the principle
that aromatase activity, which AIs target, is crucial for estrogen synthesis
Aromatase inhibitors have been used in various conditions,
including gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty in boys and girls,
and in boys with familial male-limited precocious puberty
They are also explored in combination with other treatments, such as growth hormone (GH)
for conditions like idiopathic short stature (ISS) and growth hormone deficiency
instance, a network meta-analysis compared the efficacy of GH, testosterone
, and AIs in promoting height gain in children and adolescents with ISS
Another meta-analysis specifically evaluated
the effects of combined
AIs and recombinant human GH (rhGH)
versus rhGH alone for short stature,
the result showed a better result for RHGH + AI
in summery
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are used to increase height by delaying the fusion
of growth plates in bones. The hormone estrogen, present in both sexes, is responsible for this process.
By inhibiting the aromatase enzyme, AIs reduce estrogen levels, which in turn slows down bone maturation.
This prolongs the period of linear growth, potentially leading to a greater final adult height
FOR TRT
High-dose Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
is often combined with an aromatase inhibitor (AI) to manage the conversion of testosterone to estrogen.
This conversion, mediated by the aromatase enzyme, can be significant with high testosterone doses and lead
to unwanted side effects like gynecomastia, fluid retention, and mood changes.
By blocking the aromatase enzyme, AIs such as anastrozole effectively lower estradiol (a form of estrogen) levels,
thereby preventing or reducing these estrogenic side effects. This combination therapy
is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance between testosterone and estrogen.
While estrogen is vital for male health, excessively high levels are detrimental.
The use of AIs allows for a controlled reduction in estrogen, ensuring that the benefits of TRT such as improved muscle mass
, libido, and energy are achieved without the negative consequences of estrogen dominance.
HOW TO DOSE
In the context of TRT in men,
the goal of AI co-administration is typically to prevent or manage elevated E2 levels
that can arise from the aromatization of exogenous testosterone
The average serum E2 (estradiol) level in adult men generally falls within the range of 10-50 pg/mL
which should be the ideal level after AIs
NOTE I CANT GIVE YOU AN EXACT
DOSES.THE AMOUNT
YOU SHOUD TAKE DEPEND ON BLOOD WORK
In the context of height
the level should be around 10-20 pg/mL
NOTE I CANT GIVE YOU AN EXACT
DOSES.THE AMOUNT
YOU SHOUD TAKE DEPEND ON BLOOD WORK
| Anastrozole | 1 mg/eod |
| Letrozole | 2.5 mg/eod |
| Exemestane | 12.5mg/ eod |
PLEASE NOTE
THE DOSING ABOVE
IS A BASE LINE
AJJUST ACCOUDING TO BLOOD WORK
HOW TO MINIGATE SIDE EFFECTS
Joint and Muscle Pain
Exercise: Regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises,
stretching, yoga, and resistance training, can help strengthen the muscles
around joints, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen can provide relief
Bone Loss (Osteoporosis)
Diet and Supplements: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
Exercise: Regular weight-bearing and resistance exercises
Medications: Doctors may prescribe bone-strengthening drugs, such as bisphosphonates or denosumab
Hot Flashes
Medications: If severe medications like
serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or gabapentin.
Last edited:





