Coffeebackwards
Iron
- Joined
- Sep 1, 2025
- Posts
- 151
- Reputation
- 134
Introduction:
The brow ridge and eye area are the most defining features of male attractiveness. They shape how dominant, alert, or youthful a face appears. In this thread we’ll break down the anatomy, evolution, hormonal influence, and visual cues that make this area so important. All backed by science and anthropology.
1. Basic anatomy:
2. Sexual dimorphism:
3. Hormonal influence:
4. Aesthetic ratios and visual traits:
5. Soft tissue and expression
6.Psychological impact:
7. Environment & Development:
8. Key takeaways:
Disclaimer:
Sources:
The brow ridge and eye area are the most defining features of male attractiveness. They shape how dominant, alert, or youthful a face appears. In this thread we’ll break down the anatomy, evolution, hormonal influence, and visual cues that make this area so important. All backed by science and anthropology.
1. Basic anatomy:
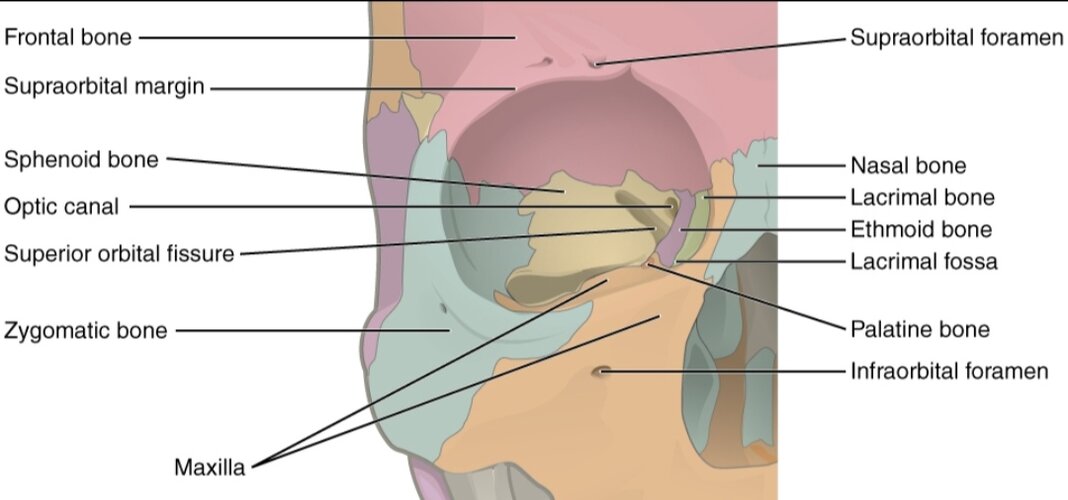
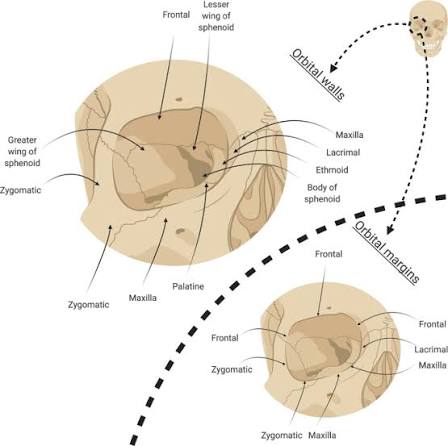
The brow ridge (also called the supraorbital ridge or torus) is the bony structure right above the eyes, mainly formed by the frontal bone. It connects to the glabella (the area between your eyebrows) and the zygomatic bones, shaping the upper midface.

The eye area, or orbital complex, includes the bones that form your eye sockets (frontal, zygomatic, sphenoid, maxillary, and ethmoid). Together, these define how deep-set or shallow your eyes look. The muscles around it: frontalis, corrugator, and orbicularis oculi are what give your brows movement and expression.

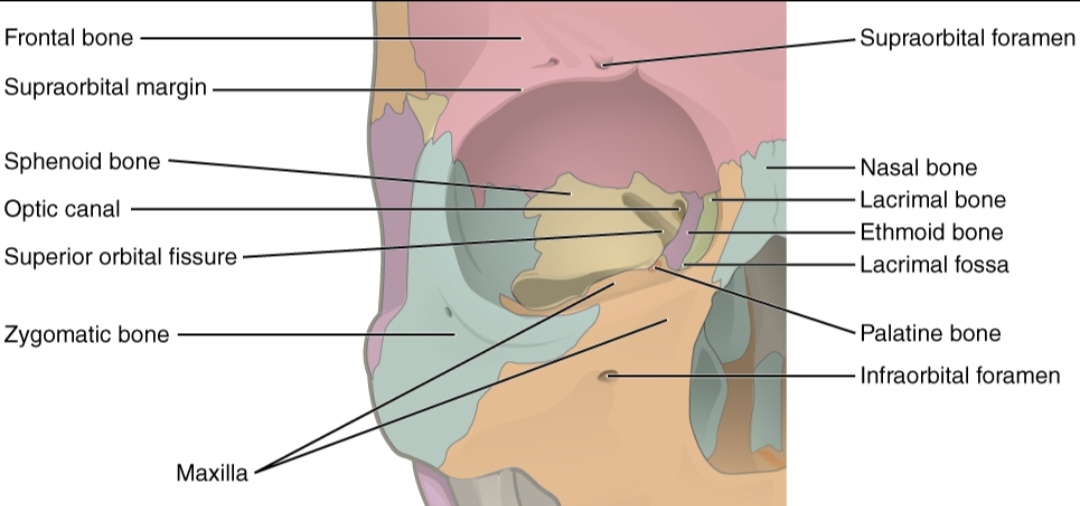
The eye area, or orbital complex, includes the bones that form your eye sockets (frontal, zygomatic, sphenoid, maxillary, and ethmoid). Together, these define how deep-set or shallow your eyes look. The muscles around it: frontalis, corrugator, and orbicularis oculi are what give your brows movement and expression.
2. Sexual dimorphism:
Men and women have different orbital and brow structures, this difference is mostly hormonal.
Men generally have heavier brow ridges, deeper set eyes, and more pronounced glabellas.
Women tend to have smoother foreheads and larger, rounder eye openings.


Why? Because during puberty, testosterone and DHT stimulate bone growth in the brow ridge and cheekbones, while estrogen causes softer, rounder features in females.
In ancient humans (E.g Homo neanderthalensis) the brow ridge was massive. Mostly for structural reasons (jaw stress distribution), but it also signaled androgen dominance and maturity. In modern humans, it’s smaller but still acts as a masculinity cue.
Men generally have heavier brow ridges, deeper set eyes, and more pronounced glabellas.
Women tend to have smoother foreheads and larger, rounder eye openings.
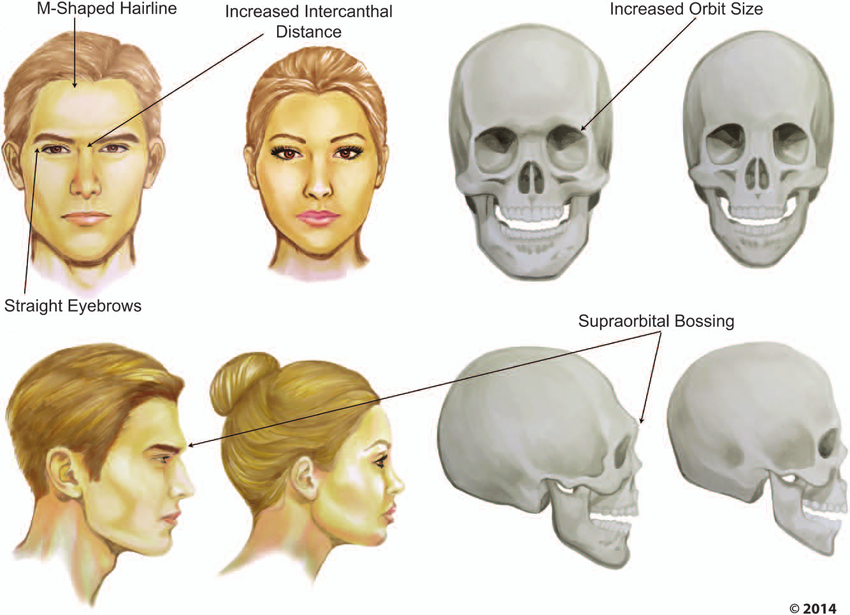
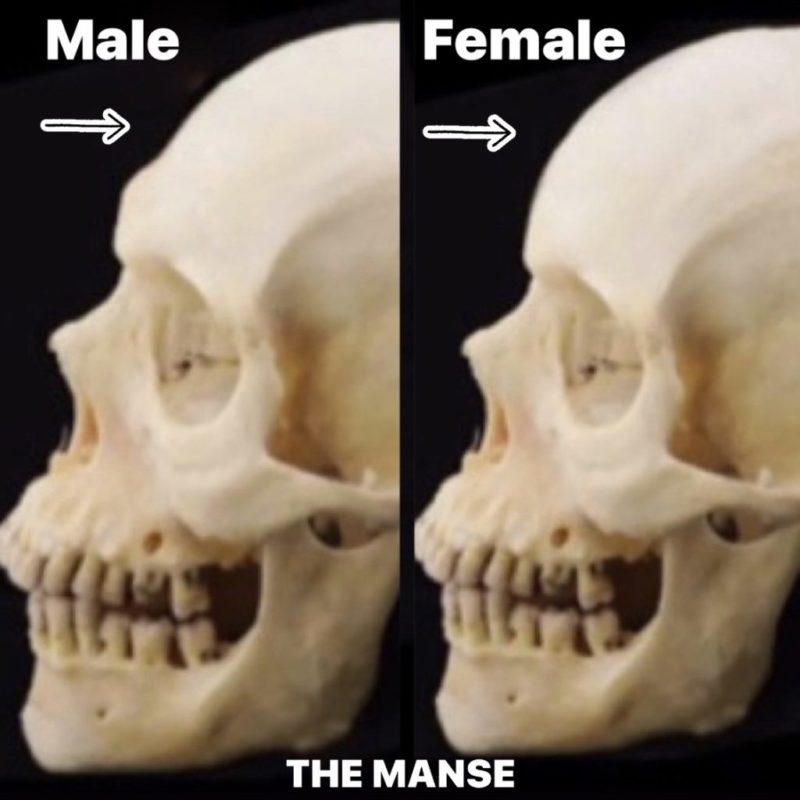
Why? Because during puberty, testosterone and DHT stimulate bone growth in the brow ridge and cheekbones, while estrogen causes softer, rounder features in females.
In ancient humans (E.g Homo neanderthalensis) the brow ridge was massive. Mostly for structural reasons (jaw stress distribution), but it also signaled androgen dominance and maturity. In modern humans, it’s smaller but still acts as a masculinity cue.
3. Hormonal influence:
Facial bone structure is mainly set during puberty and depends on hormonal balance:
Testosterone/DHT - stimulates bone growth and thickens the supraorbital ridge.
Growth Hormone (GH) and IGF-1 - increase overall craniofacial size and bone remodeling.
Estrogen - controls bone maturation and growth plate closure.
Cortisol & Thyroid imbalance - can thin skin, change fat distribution, or cause orbital puffiness.

In short, the androgen to estrogen ratio during your teenage years decides how much your brow and eye area set into that masculine, hunter type eye structure.
Testosterone/DHT - stimulates bone growth and thickens the supraorbital ridge.
Growth Hormone (GH) and IGF-1 - increase overall craniofacial size and bone remodeling.
Estrogen - controls bone maturation and growth plate closure.
Cortisol & Thyroid imbalance - can thin skin, change fat distribution, or cause orbital puffiness.
In short, the androgen to estrogen ratio during your teenage years decides how much your brow and eye area set into that masculine, hunter type eye structure.
4. Aesthetic ratios and visual traits:
Some key ratios that determine how masculine or aesthetic the eye area looks:
Orbital depth, deeper eyes = more shadow contrast = more masculine.

Eye to brow distance, lower = stronger dominance perception.

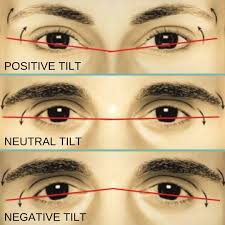
Canthal tilt, upward tilt = youth and energy, downward tilt = tired or aged look.

Supraorbital projection, a pronounced ridge adds contour and bone contrast under lighting.
The hunter eyes that people talk about is essentially good orbital depth, low eye to brow distance, and shadowed contrast created by bone shape and lighting.
Orbital depth, deeper eyes = more shadow contrast = more masculine.
Eye to brow distance, lower = stronger dominance perception.

Canthal tilt, upward tilt = youth and energy, downward tilt = tired or aged look.
Supraorbital projection, a pronounced ridge adds contour and bone contrast under lighting.
The hunter eyes that people talk about is essentially good orbital depth, low eye to brow distance, and shadowed contrast created by bone shape and lighting.
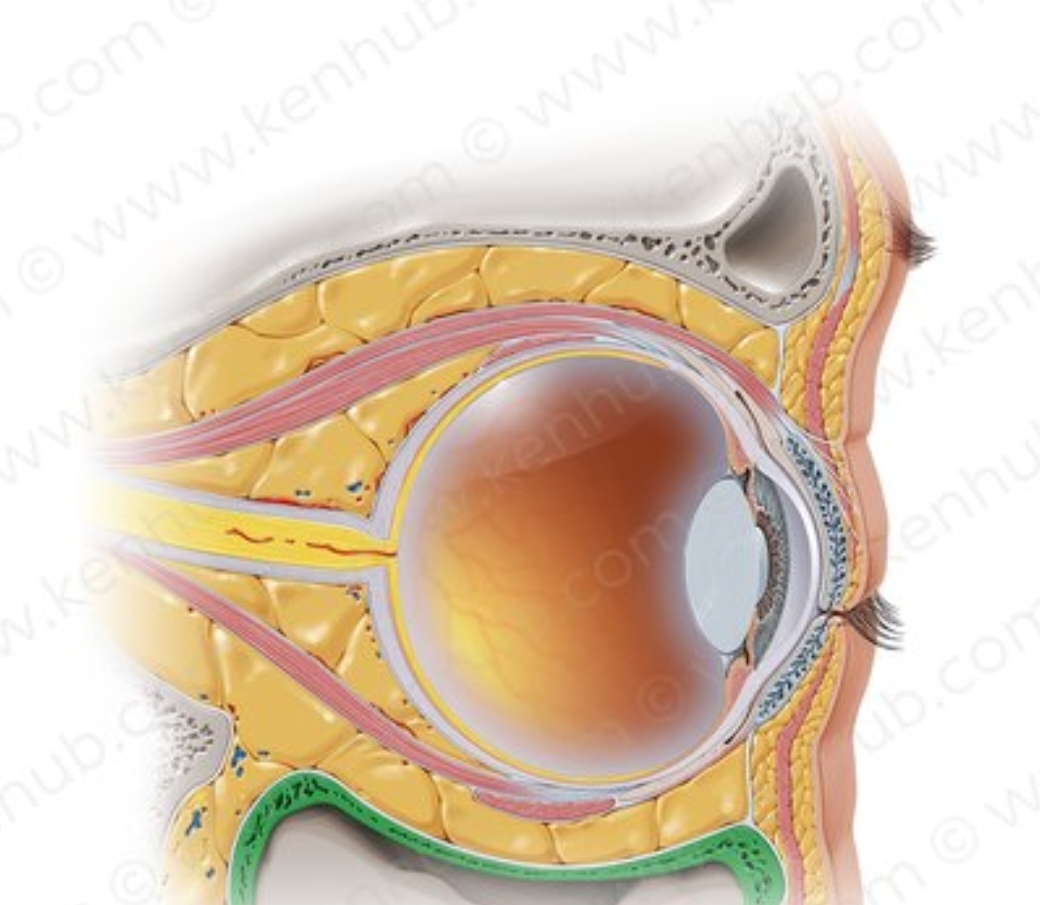
5. Soft tissue and expression
Even if your bone structure is ideal, the soft tissue layer can change how it appears:
Too much fat around the upper orbit can make eyes look puffy or less deep set.

The levator palpebrae and orbicularis muscles affect how your eyelid creases and how awake your eyes look.
Brow position and movement (mainly through the frontalis) also affect perceived dominance, relaxed brows = calm look, raised brows = submissive or surprised look.
This is why fat loss, sleep, and even posture (forward head posture ruins the shadowing effect) make a huge visual difference without any
surgery.
Too much fat around the upper orbit can make eyes look puffy or less deep set.
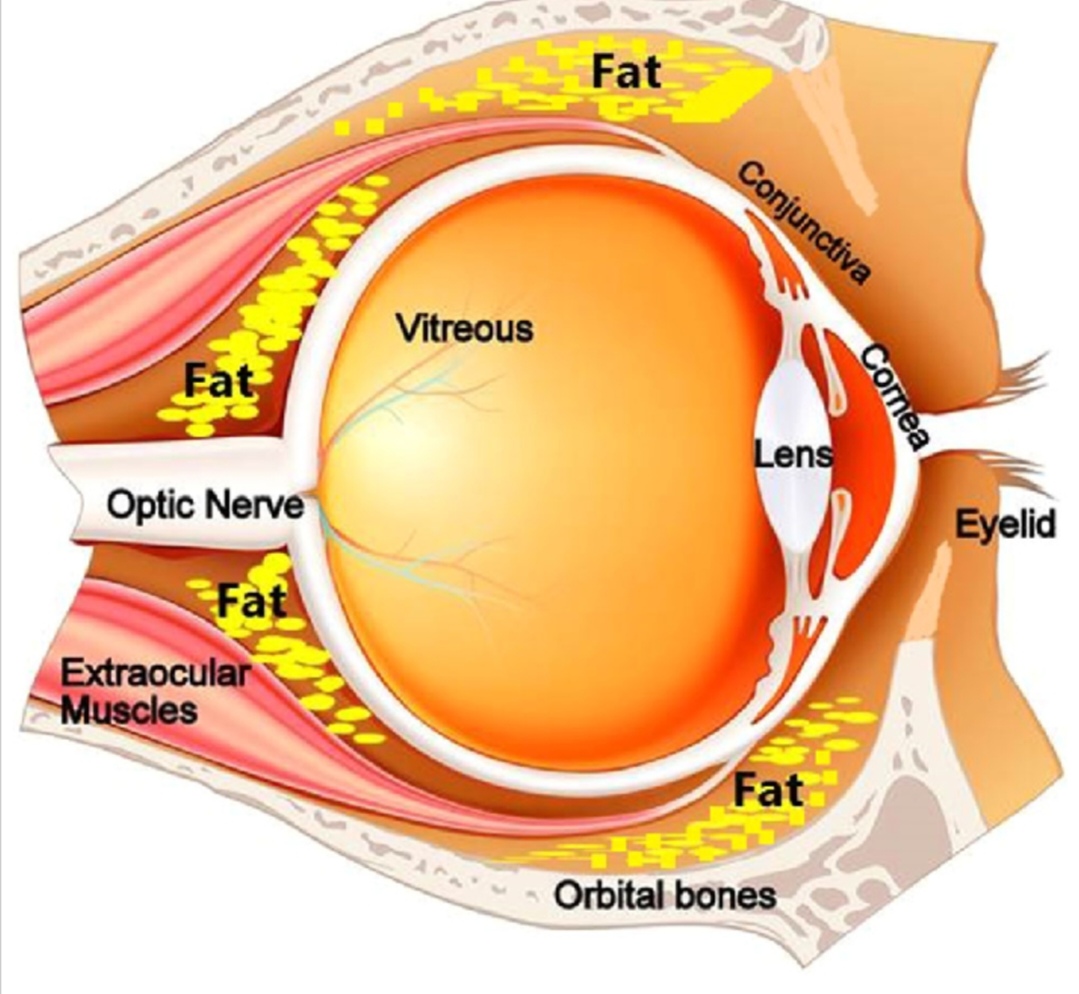
The levator palpebrae and orbicularis muscles affect how your eyelid creases and how awake your eyes look.
Brow position and movement (mainly through the frontalis) also affect perceived dominance, relaxed brows = calm look, raised brows = submissive or surprised look.
This is why fat loss, sleep, and even posture (forward head posture ruins the shadowing effect) make a huge visual difference without any
surgery.
6.Psychological impact:
The human brain is wired to instantly read dominance and vitality from the eye area.
Lower set brows and deeper eyes signal confidence, strength, focus and intimidation.
High set brows and wide eyes read as open, friendly, or submissive.


Studies using FMRI show that faces with strong brow ridges trigger more activity in the amygdala (the brain’s attention center) people find them more memorable or commanding.
That’s why this part of the face is so important for overall presence.
Lower set brows and deeper eyes signal confidence, strength, focus and intimidation.
High set brows and wide eyes read as open, friendly, or submissive.


Studies using FMRI show that faces with strong brow ridges trigger more activity in the amygdala (the brain’s attention center) people find them more memorable or commanding.
That’s why this part of the face is so important for overall presence.
7. Environment & Development:
You can’t fully change your bone structure after puberty, but a lot of visual cues can still be improved.
Things that influence the orbital area:
Vitamin D and nutrition - affect bone and collagen health. ( If you're young I recommend you getting enough of everything your body needs. )
Sleep and caffeine- prevents periorbital puffiness and dark circles.
Posture - a forward head tilt can make your eyes look more recessed.
Fat distribution - lower body fat sharpens orbital definition.
Lighting and eyebrow shape also play huge roles in how your orbital structure is perceived.
Things that influence the orbital area:
Vitamin D and nutrition - affect bone and collagen health. ( If you're young I recommend you getting enough of everything your body needs. )
Sleep and caffeine- prevents periorbital puffiness and dark circles.
Posture - a forward head tilt can make your eyes look more recessed.
Fat distribution - lower body fat sharpens orbital definition.
Lighting and eyebrow shape also play huge roles in how your orbital structure is perceived.
8. Key takeaways:
The brow ridge and eyes are the core of male facial dimorphism, here's a difference between good eye are but bad features and bad eye are but good features.


They’re heavily influenced by testosterone, GH, and overall development.
The right ratios, depth, and shadow contrast create the ideal hunter eye aesthetic.
You can’t fully remodel bone after puberty (You can't do so even when you're in puberty, a lot of it is genetics and you will probably need surgery to achieve the perfect eye area if you don't have it already), but you can enhance perception through fat reduction, expression control, and lighting awareness.(Basically frauding the look)
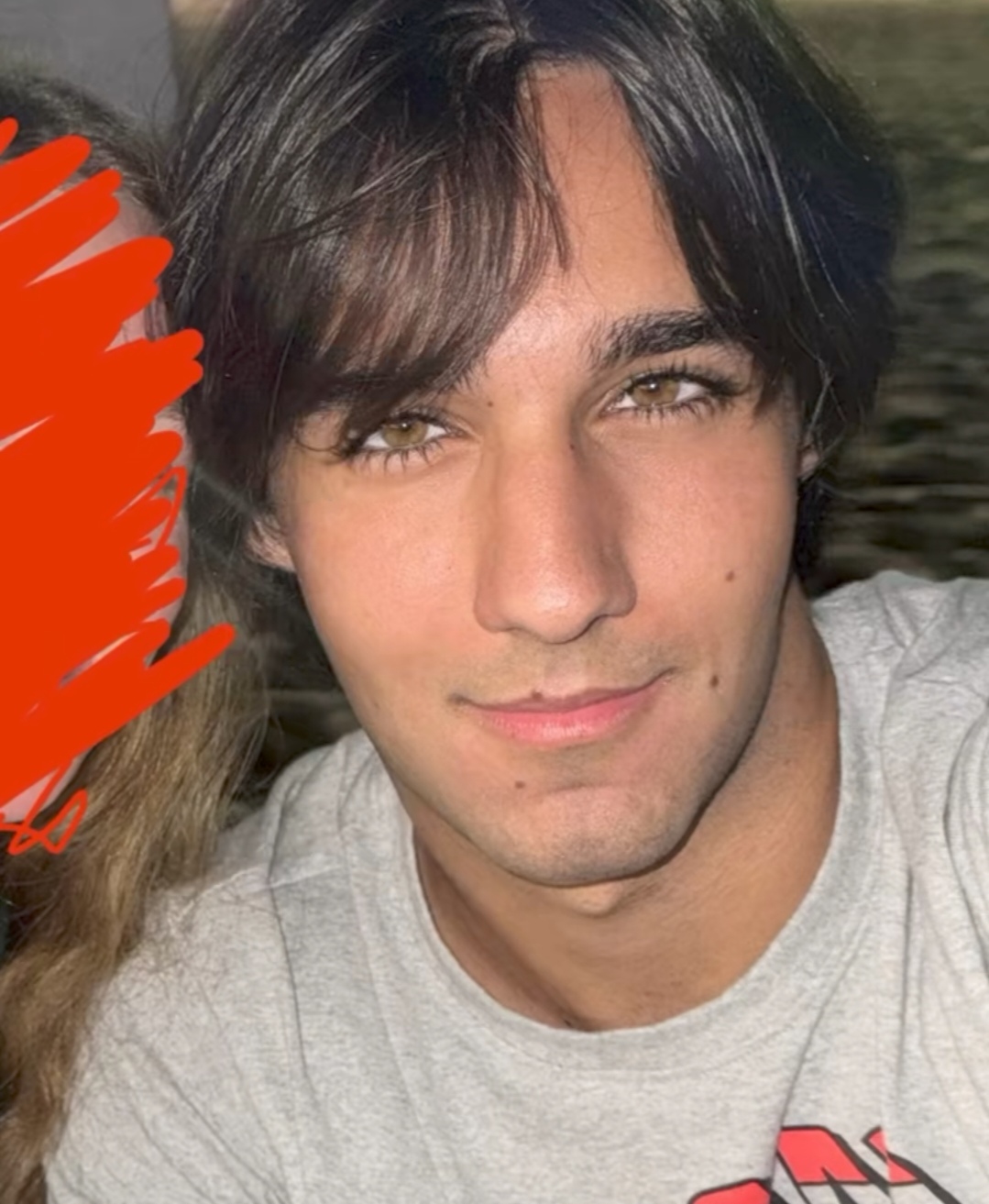
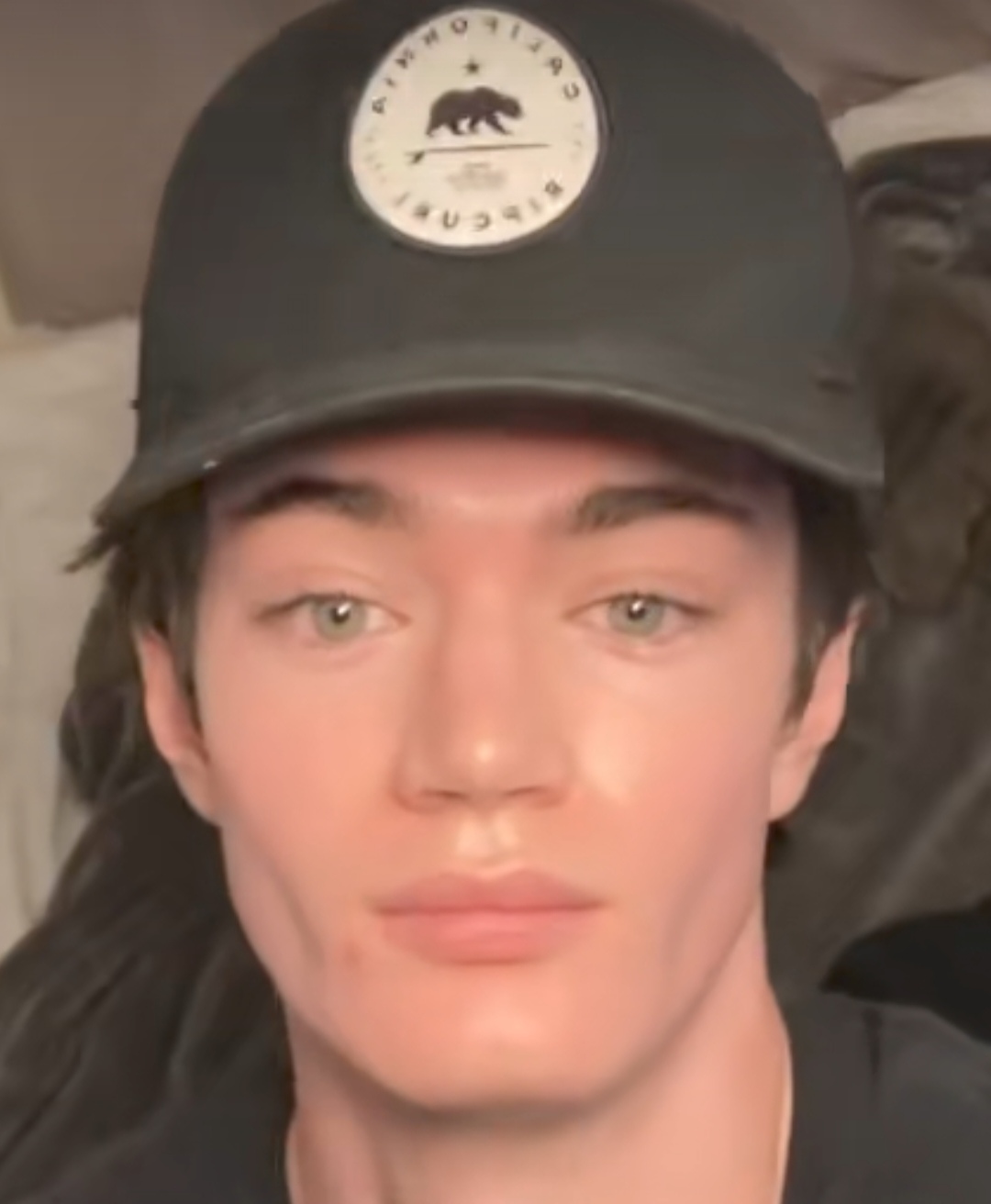


They’re heavily influenced by testosterone, GH, and overall development.
The right ratios, depth, and shadow contrast create the ideal hunter eye aesthetic.
You can’t fully remodel bone after puberty (You can't do so even when you're in puberty, a lot of it is genetics and you will probably need surgery to achieve the perfect eye area if you don't have it already), but you can enhance perception through fat reduction, expression control, and lighting awareness.(Basically frauding the look)
Disclaimer:
This post is for educational and research purposes only.
None of this is medical advice or encouragement to use hormonal or surgical methods.
Always do your own research before trying something.
(I'm still figuring .org out so my threads might not be as good as others, feel free to tell me how I should improve my threads.)
None of this is medical advice or encouragement to use hormonal or surgical methods.
Always do your own research before trying something.
(I'm still figuring .org out so my threads might not be as good as others, feel free to tell me how I should improve my threads.)
Sources:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-43007-y
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-018-0528-0
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0018506X11002157
https://eyewiki.org/Orbital_Adipose_Tissue
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19730316/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0018506X11002157
https://saxonmd.com/blog/can-men-get-a-brow-bone-reduction-prominent-brow-ridge/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brow_ridge
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/bones-of-the-orbit
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539843/
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-018-0528-0
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0018506X11002157
https://eyewiki.org/Orbital_Adipose_Tissue
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19730316/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0018506X11002157
https://saxonmd.com/blog/can-men-get-a-brow-bone-reduction-prominent-brow-ridge/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brow_ridge
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/bones-of-the-orbit
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539843/