Coffeebackwards
Iron
- Joined
- Sep 1, 2025
- Posts
- 150
- Reputation
- 131
What is Enclomiphene?
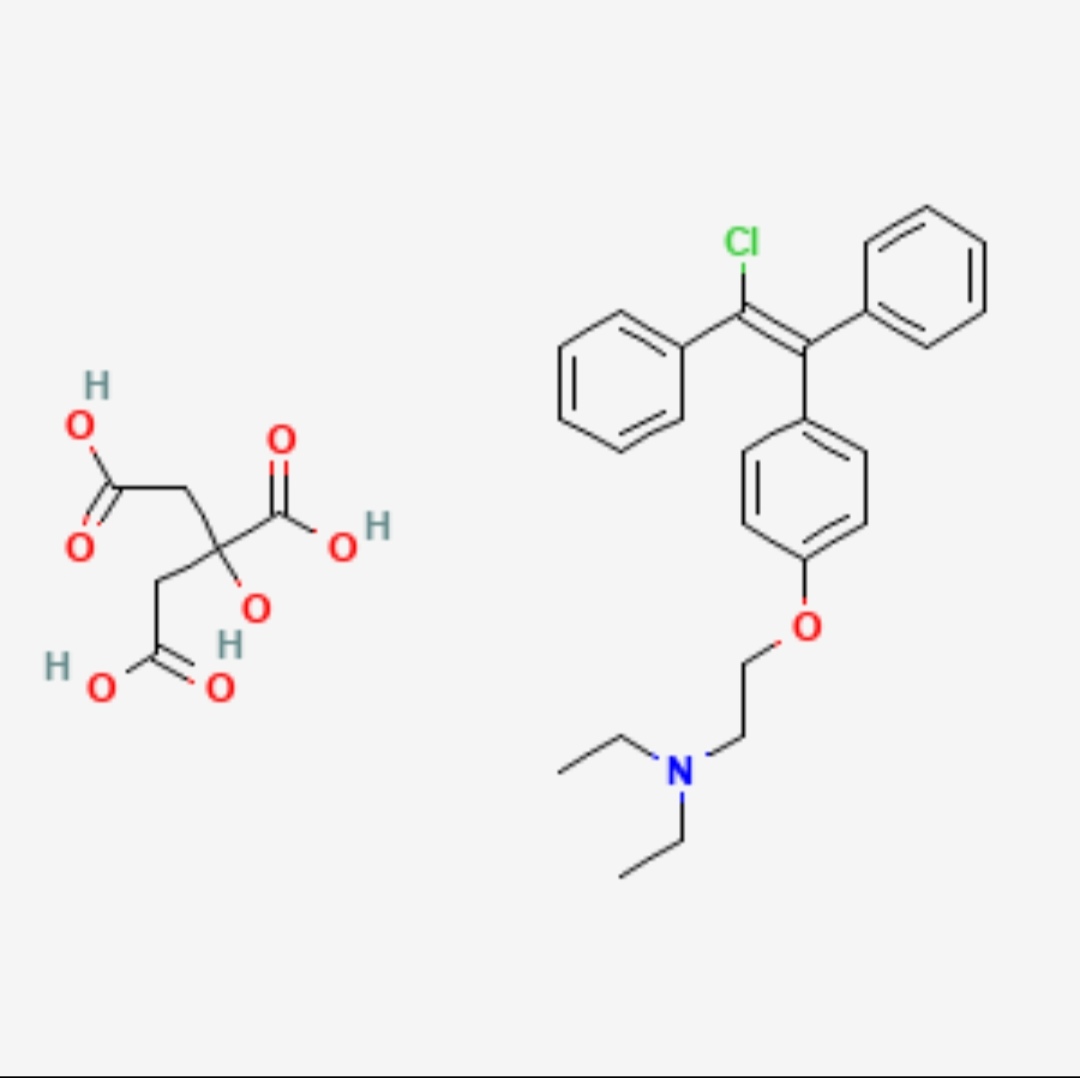
Enclomiphene is an SERM (selective estragon receptor modulator)
Unlike tamoxifen ( another SERM), Enclomiphene is designed to specifically raise testosterone without as many estrogen related side effects.
If you're wondering, no it's not exogenous testosterone. Meaning it doesn't replace your natural T. It stimulates your body to make more naturally.
How does it work?
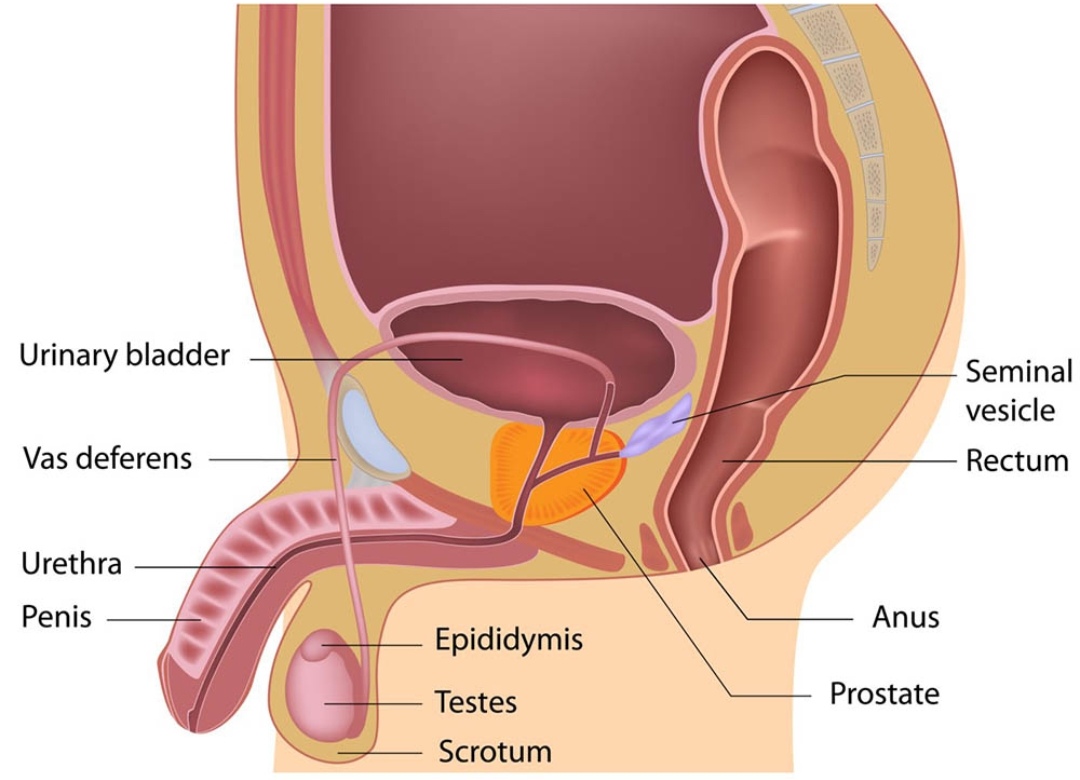
1. Hypothalamus interaction
Enclomiphene blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus.
Normally, estrogen feeds back to the hypothalamus to signal that there is enough testosterone already.
2. Pituary activation
By blocking this signal, the hypothalamus thinks testosterone is low. Then the hypothalamus releases GnRH ( gonadotropin-releasing hormone).
GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH and FSH.
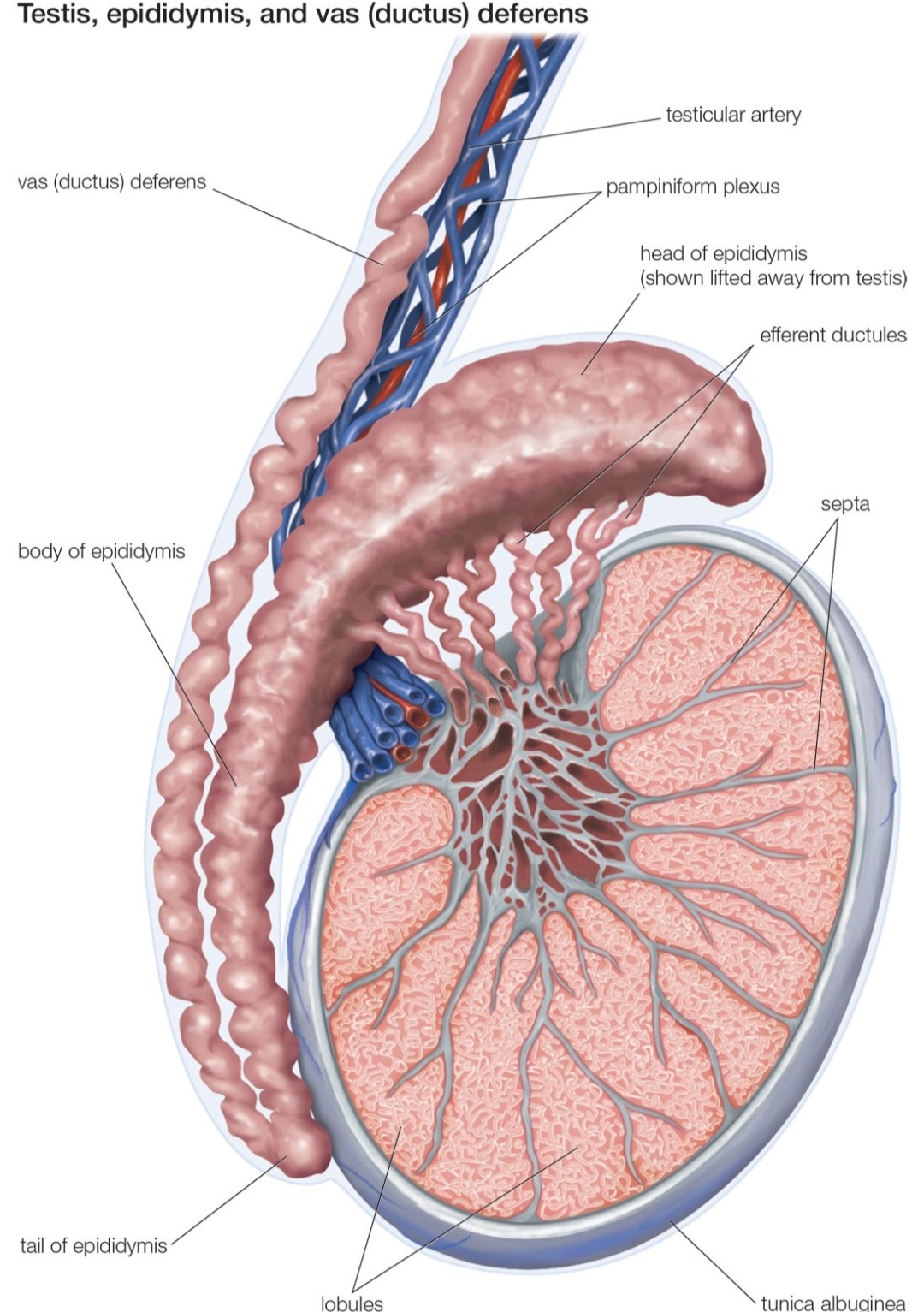
3. Testicular response
LH signals leydig cells in the testes to produce more testosterone
FSH supports spermatogenesis, maintaining fertility
Results: Higher endogenous testosterone without shutting down the testes ( unlike TRT)
How does it affect the body?
1. Muscle mass: more androgen = better protein synthesis
2. Fat distribution: Testosterone favors lean mass and reduces visceral fat.
3. Libido/mood:
Testosterone elevation improved energy, confidence and sex drive ( you'll basically become a walking sex machine )
KEY POINT:
unlike exogenous T, enclomiphene preserves HPTA function, so testes don't shrink and fertility is maintained.
How is it different from clomiphene citrate?
Clomiphene is a mixture of two isomers:
Enclomiphene - pure activating isomer, meaning: faster testosterone increase, less risk of estrogen related side effects, more predictable lab outcomes.
zuclomiphene ( can cause estrogenic side effects ) - you don't have to worry about it since you'd only be taking Enclomiphene.
Studies in men with secondary hypogonadism have shown that testosterone levels rise within 2-4 weeks, fertility is maintained, estradiol may rise but it's usually within normal range.
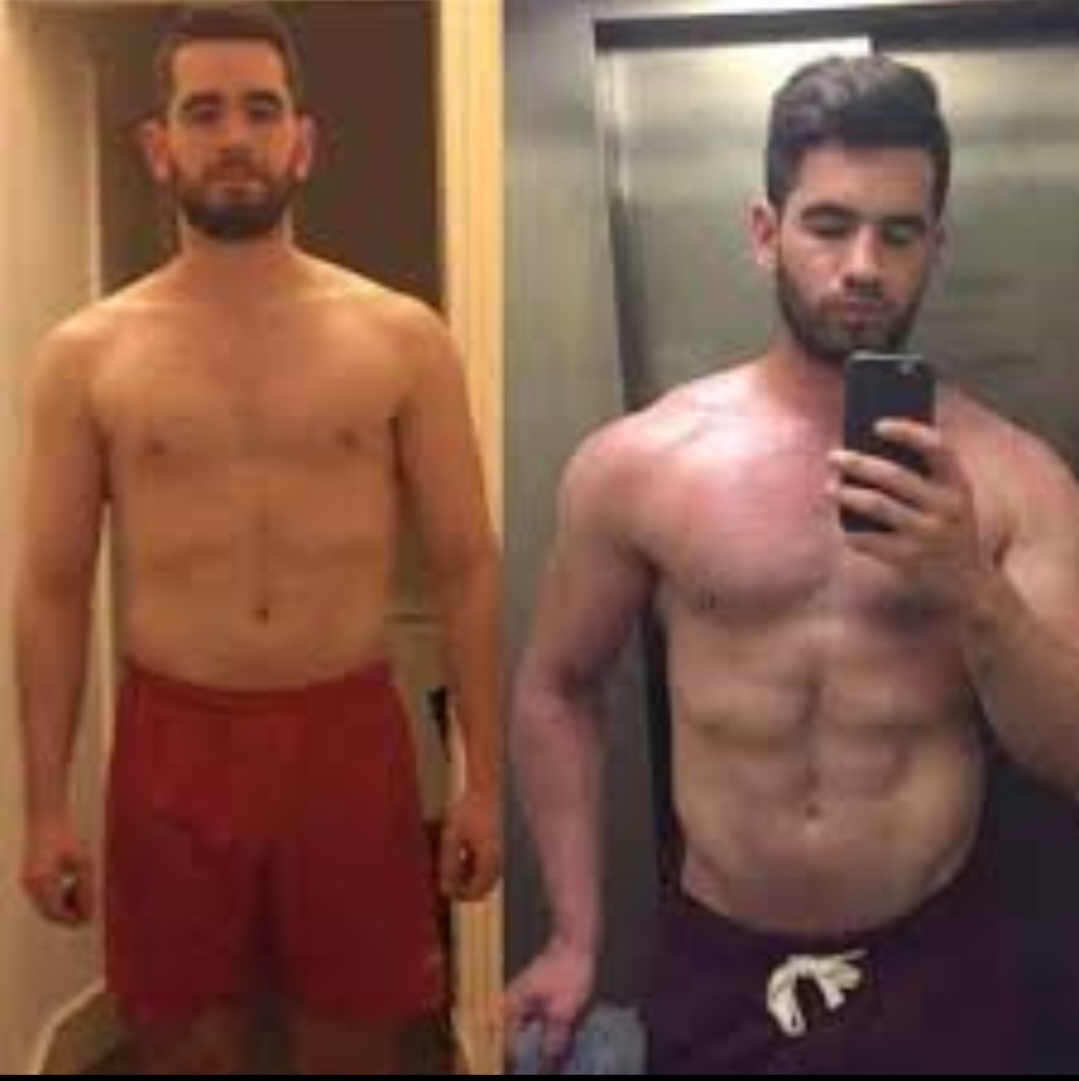
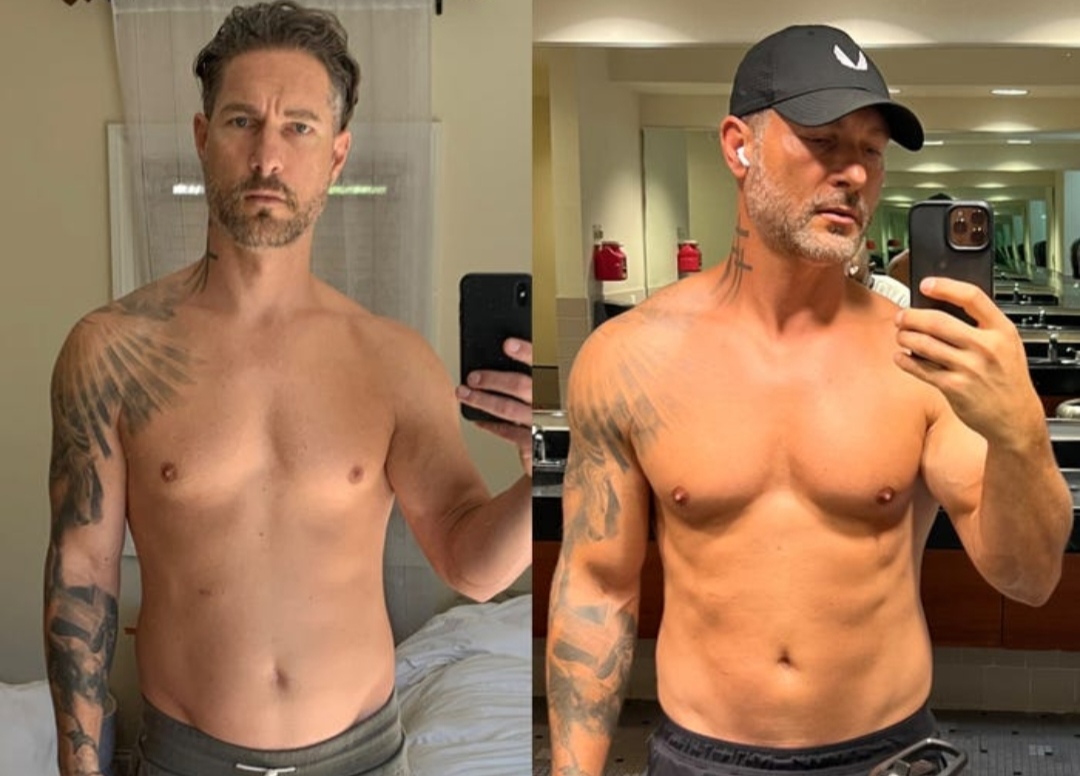
Here are 2 Prime examples before and after using Enclomiphene:


Key takeaways:
Enclomiphene is not a steroid, it's a hormone modulator.
Works by tricking your brain into making more testosterone naturally.
Effects:
better muscle to fat ratio, slight facial improvements, more energy.
Requires proper dosage to avoid estrogen rebound or other side effects. ( Sadly I'm not knowledgeable enough to give you a full dosage breakdown )
Disclaimer:
I am not promoting Enclomiphene or encouraging anyone to use it.
This post is purely for research and educational purposes.
If you are planning to use Enclomiphene, please do your own research.
( This is my first proper post so if you have any tips on how to improve my threads please tell me )
Sources:
https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB067...01&phase=3&purpose=treatment&status=completed
https://www.news-medical.net/life-s...hanism-efficacy-and-safety-consideration.aspx
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25044085
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enclomifene
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5009465
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4155868
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11491226
https://academic.oup.com/jsm/article/21/Supplement_1/qdae001.090/7600907
https://www.hims.com/blog/what-is-enclomiphene
Enclomiphene is an SERM (selective estragon receptor modulator)
Unlike tamoxifen ( another SERM), Enclomiphene is designed to specifically raise testosterone without as many estrogen related side effects.
If you're wondering, no it's not exogenous testosterone. Meaning it doesn't replace your natural T. It stimulates your body to make more naturally.

How does it work?
1. Hypothalamus interaction
Enclomiphene blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus.
Normally, estrogen feeds back to the hypothalamus to signal that there is enough testosterone already.
2. Pituary activation
By blocking this signal, the hypothalamus thinks testosterone is low. Then the hypothalamus releases GnRH ( gonadotropin-releasing hormone).
GnRH stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH and FSH.
3. Testicular response
LH signals leydig cells in the testes to produce more testosterone
FSH supports spermatogenesis, maintaining fertility
Results: Higher endogenous testosterone without shutting down the testes ( unlike TRT)



How does it affect the body?
1. Muscle mass: more androgen = better protein synthesis
2. Fat distribution: Testosterone favors lean mass and reduces visceral fat.
3. Libido/mood:
Testosterone elevation improved energy, confidence and sex drive ( you'll basically become a walking sex machine )
KEY POINT:
unlike exogenous T, enclomiphene preserves HPTA function, so testes don't shrink and fertility is maintained.
How is it different from clomiphene citrate?
Clomiphene is a mixture of two isomers:
Enclomiphene - pure activating isomer, meaning: faster testosterone increase, less risk of estrogen related side effects, more predictable lab outcomes.
zuclomiphene ( can cause estrogenic side effects ) - you don't have to worry about it since you'd only be taking Enclomiphene.
Studies in men with secondary hypogonadism have shown that testosterone levels rise within 2-4 weeks, fertility is maintained, estradiol may rise but it's usually within normal range.
Here are 2 Prime examples before and after using Enclomiphene:


Key takeaways:
Enclomiphene is not a steroid, it's a hormone modulator.
Works by tricking your brain into making more testosterone naturally.
Effects:
better muscle to fat ratio, slight facial improvements, more energy.
Requires proper dosage to avoid estrogen rebound or other side effects. ( Sadly I'm not knowledgeable enough to give you a full dosage breakdown )
Disclaimer:
I am not promoting Enclomiphene or encouraging anyone to use it.
This post is purely for research and educational purposes.
If you are planning to use Enclomiphene, please do your own research.
( This is my first proper post so if you have any tips on how to improve my threads please tell me )
Sources:
https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB067...01&phase=3&purpose=treatment&status=completed
https://www.news-medical.net/life-s...hanism-efficacy-and-safety-consideration.aspx
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25044085
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enclomifene
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5009465
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4155868
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11491226
https://academic.oup.com/jsm/article/21/Supplement_1/qdae001.090/7600907
https://www.hims.com/blog/what-is-enclomiphene

