ihatemySOST
Bronze
- Joined
- Sep 5, 2025
- Posts
- 438
- Reputation
- 665
The never-ending debate in this community has always been: Does bone smashing actually work? Unfortunately, when people try to prove it, they almost always rely on Wolff’s law. All that Wolff’s law states is that trabecular and cortical bone increase in density when exposed to mechanical stress (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499863/). It never says anything about bones increasing in size as a result of trauma.
On the other side, those who argue that it doesn’t work usually bring up weak points as well, saying that bone only increases in density, not size, and that bones need controlled, physiological types of stress to adapt, such as chewing, running, or exercising, rather than random hits.
So in the end, whether it’s the people who believe bone smashing works or those who completely dismiss it, both sides usually end up presenting weak arguments.
So thats leave the question: does bone smashing actually work
this post will divide to Tow parts
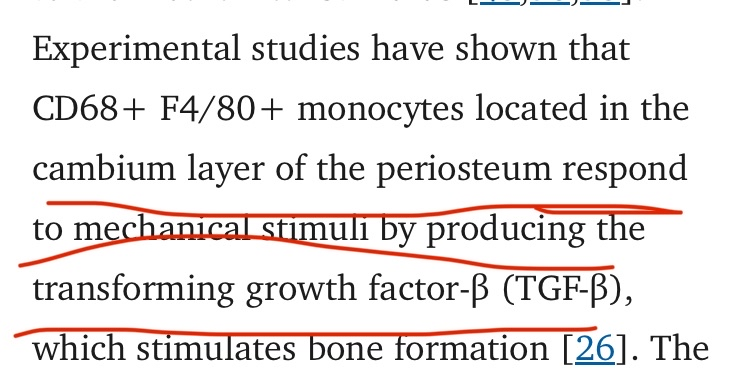
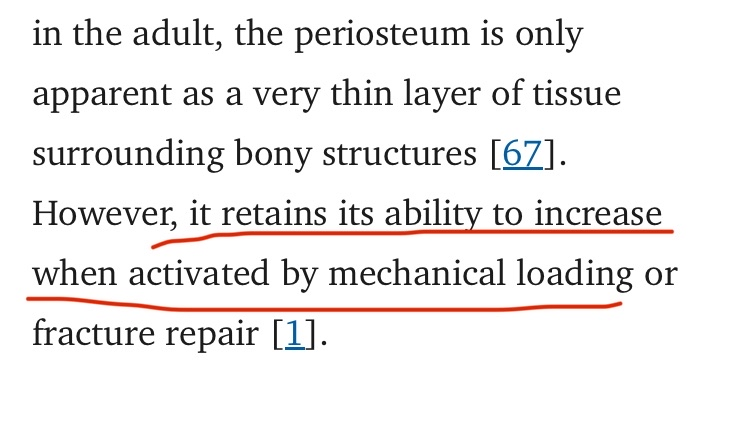
In the beginning, when a bone is struck directly, small blood vessels known as subperiosteal capillaries can rupture. Once these vessels break, blood leaks out and forms what is called a subperiosteal hematoma. This condition causes the periosteum to lift away from the cortical bone, creating an inflammatory space between the cortical bone and the periosteum.
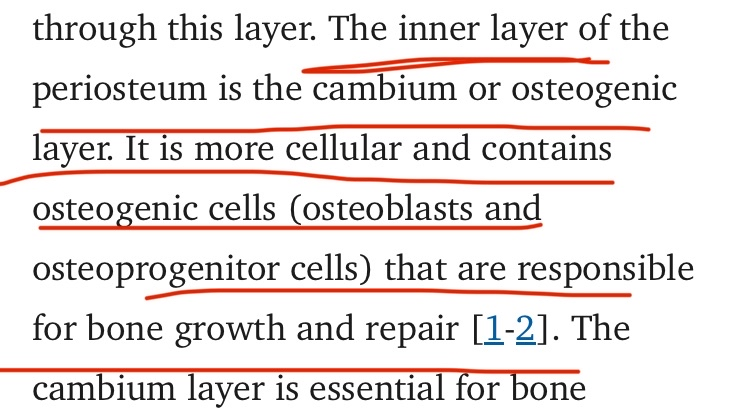
The periosteum itself has an inner layer called the cambium, which is very rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and immature osteoblasts. Under normal conditions this layer remains relatively inactive, but it quickly becomes activated when the periosteum is lifted away from the cortex.
This elevation of the periosteum triggers an increase in the expression of Runx2, TGF-β2, and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The activation of these pathways rapidly recruits immature osteoblasts to mature into active bone-forming cells, while also driving osteoprogenitor cells to differentiate into new osteoblasts. As a result, the hematoma that formed between the periosteum and the cortex begins to calcify, leading to the formation of a new bony layer.






Sources:
-https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11786143/
-
https://sharondewitte.wordpress.com...-and-healed-periosteal-new-bone-formation.pdf
Summary: When a bone receives a direct trauam, the blood vessels rupture, leading to the formation of a subperiosteal hematoma. This lifts the periosteum, and eventually the hematoma calcifies and transforms into new bone
So after reading this, ask yourself: isn’t the swelling and bulge caused by bone smashing the clearest evidence of its effectiveness according to bone biology? Luckily, the answer is: yes.
so now i will move to part 2 :
I will show alot of studies to prove my point, so get ready please.
Study #1

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
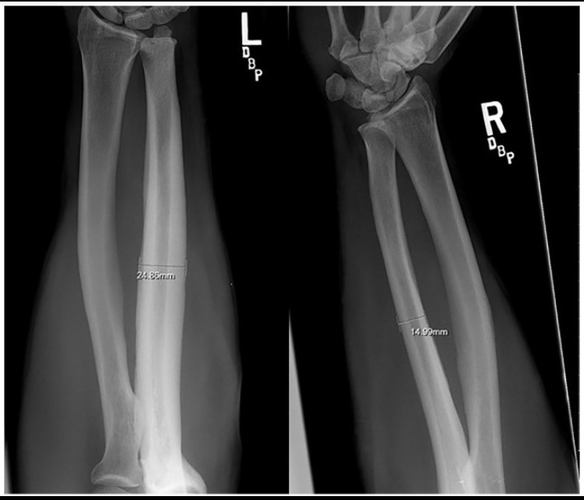
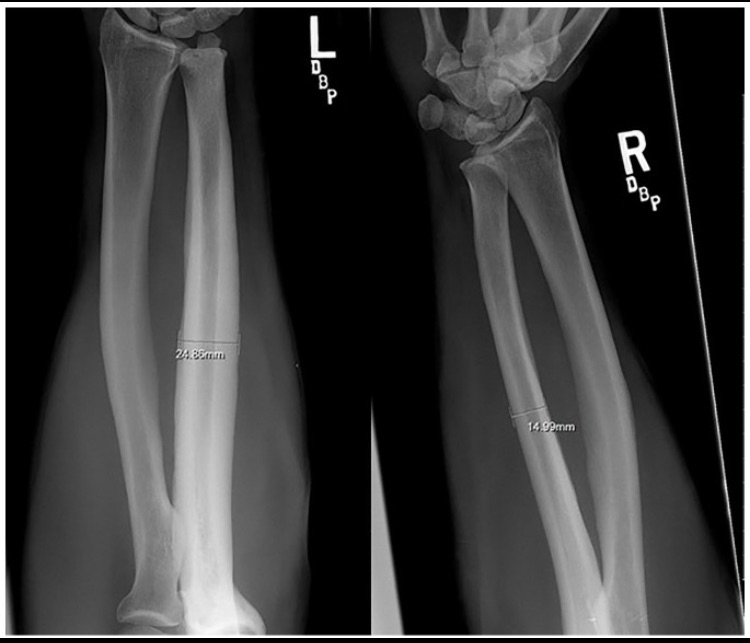
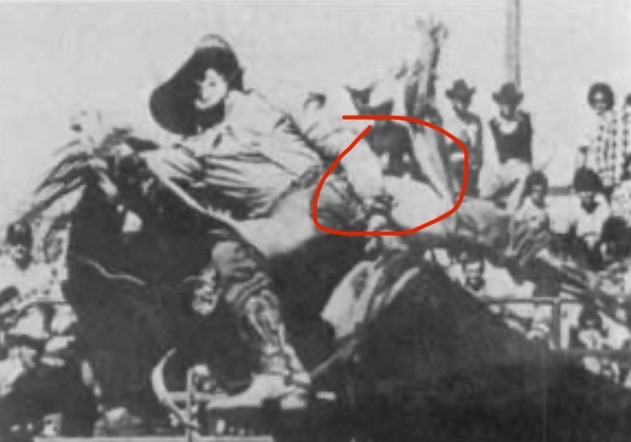
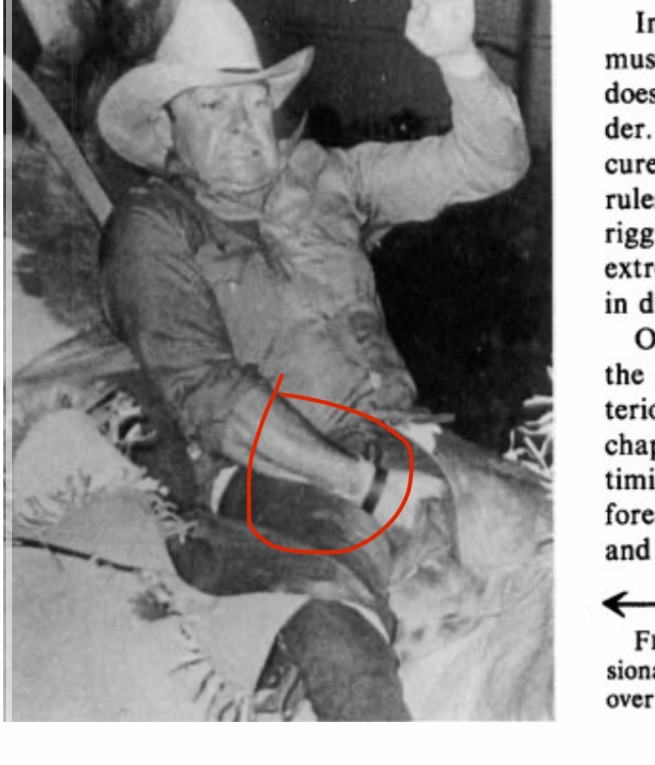
This study examined professional bareback rodeo riders (without a saddle), showing extreme bone hypertrophy in the ulna. The hypertrophy results from direct trauma and impact with the hip bone. For perspective, some individuals had up to a 92% increase in bone diameter and a 268% increase in cross-sectional area, which is extremely unusual. The image in the study shows significant hypertrophy, though not the individual with nearly doubled bone diameter.
If anyone claims this hypertrophy is caused by muscle pull alone, that is incorrect. The main reason is direct trauma to the bone, supported by the following:


Study #2
https://reader.z-library.sk/read/bc...4f5ca2d25511e411cd99274aaa2a01e1e75af408e60e1
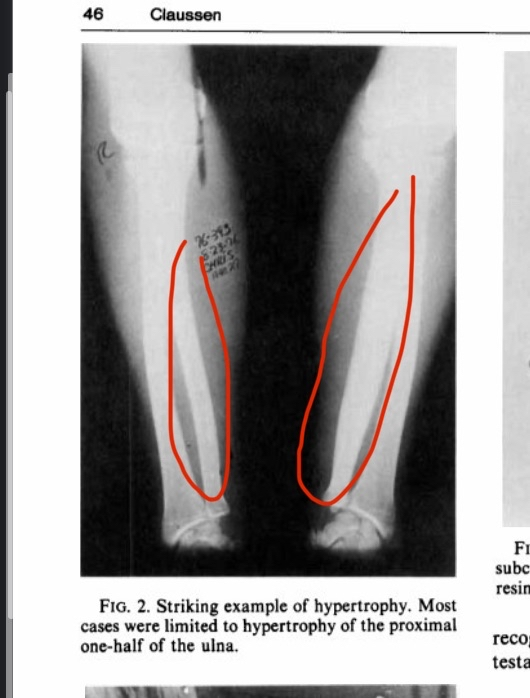
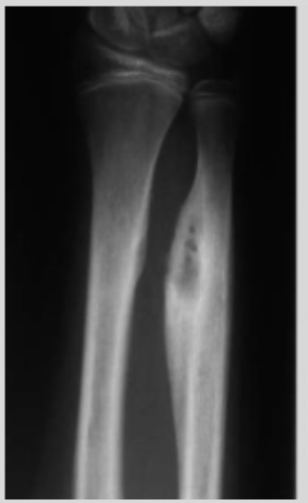
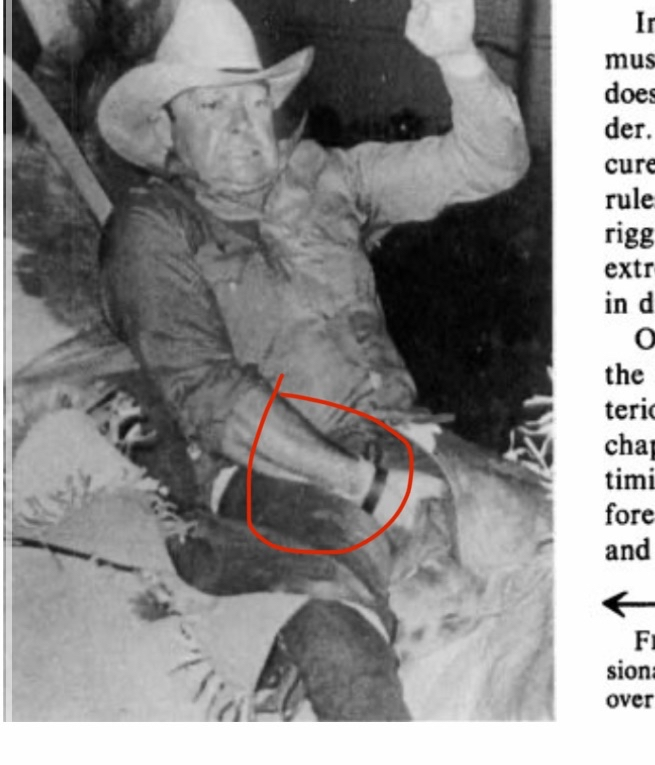
Honestly, this is personally my favorite study to prove the effectiveness of bone smashing. This study was conducted in 1980 on 60 participants, 37 of whom were professional riders without a saddle. Guess what? As I mentioned before, significant bone hypertrophy occurred only in those who practiced horseback riding without a saddle (I explained the reason before, because this type requires the rider’s ulna to hit and contact the hip). To understand more about this process that happens during the race, here is a direct quote from the study:
“On observing a contestant who is riding, the riding arm is noted to contact the anterior iliac crest and the heavily resined chaps (Fig. 3). The event requires strength, timing, balance, and courage. Ideally, the forearm should be tucked against the pelvis and chaps. Failure to maintain this position, resulting in hammering action of the forearm against pelvis and chaps.”
Oh my God, I can’t believe it, the scientists literally wrote “hammering action”! Who would believe this? Hammering movements on the bone cause severe bone hypertrophy. Wait, what does this remind you of? Yes, exactly the same thing you were trying to prove wrong, which is hammering your face. And luckily, the scientists also mentioned that bone hypertrophy occurred due to periosteal inflammation resulting from trauma to the bone. Yes, literally. You can look at the image below and you will notice severe bone hypertrophy at the place where the ulna hits the hip. Oh my God, all this hypertrophy happens in just an 8-second round!!! Just this very short time is enough to cause extreme bone growth. The answer is yes, lol



Study #3
 www.nature.com
www.nature.com
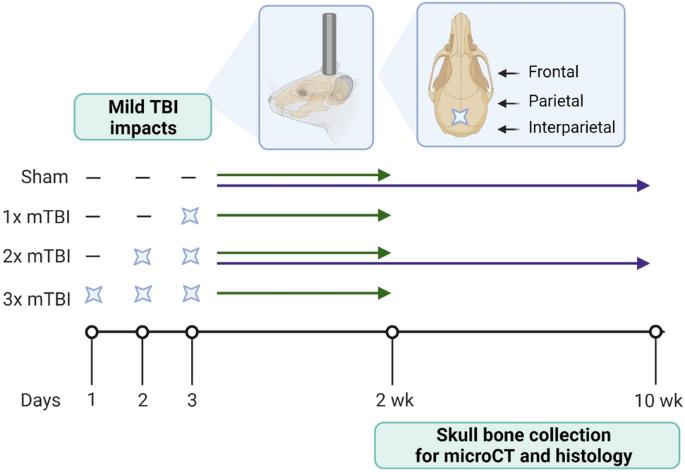
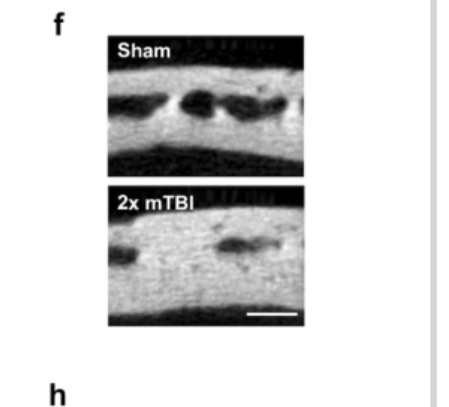
The scientists wanted to study the effect of direct impacts on bone shape in skull bones. They designed a device to deliver a direct impact to the bone. They applied the impact only twice (just two light hits) and measured after two weeks and after ten weeks. After two weeks, there was mild bone hypertrophy, but after ten weeks, there was severe and very clear bone hypertrophy. This shows that the effects on bone hypertrophy continued to increase even after only two impacts. The study also mentioned that bone hypertrophy could occur due to trauma.
Study #4

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
The scientists reported that some children had increased thickness in the midshaft of the femur, and they stated that the cause of some of these cases was direct trauma to the bone.

Therefore, this is evidence that direct trauma can cause bone hypertrophy.
Study #5

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Once again, the scientists observed hypertrophy of the cortical bone due to direct trauma to the bone.

Study #6
 pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
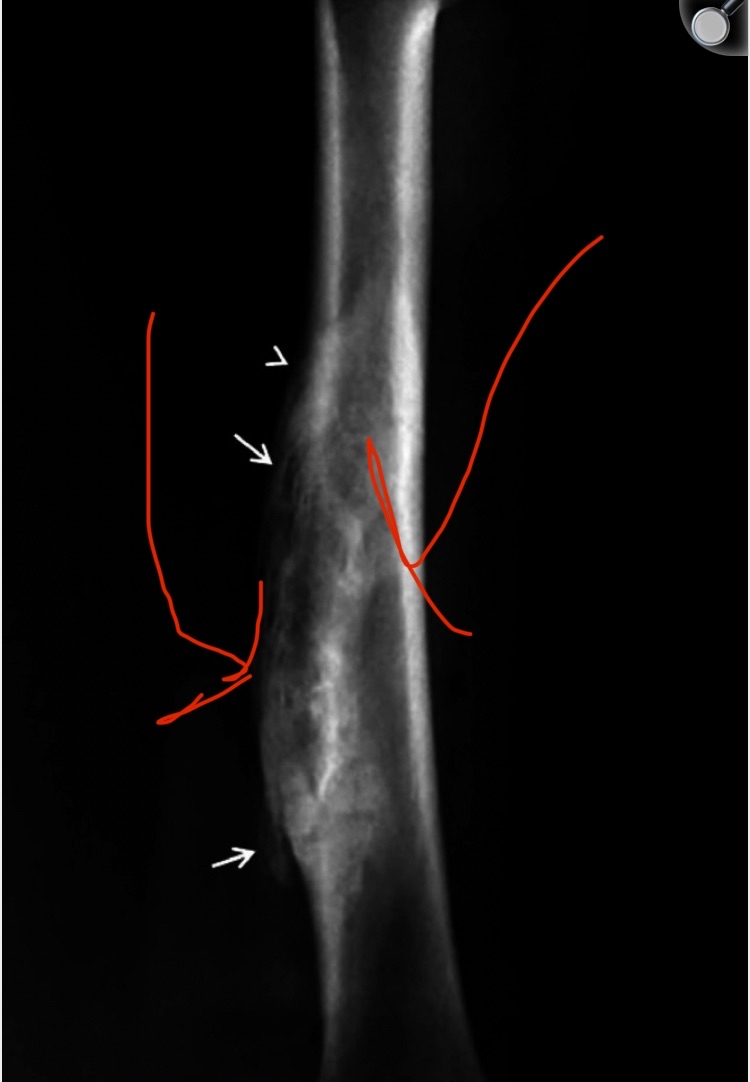
A 15-year-old child experienced direct trauma to his femur (yes, the scientists literally mentioned direct trauma). You can look at the image below, where you will find severe bone hypertrophy at the site of the injury.
Org does now allow me for add more photos after this , so i will share the studies without photos , if u want to see the bone hypertrophy, click in the link
Study #6
 pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
A 15-year-old child experienced direct trauma to his femur (yes, the scientists literally mentioned direct trauma). You can look at the image below, where you will find severe bone hypertrophy at the site of the direct trauma
Study #7
 clinmedjournals.org
clinmedjournals.org
A case report on a Lacrosse player (this sport requires direct contact with the opponent to gain possession of the ball). The player reported pain in the area left exposed “between his shoulder and elbow pads”. Because the area was exposed, it was subjected to direct trauma, which caused a subperiosteal hematoma. Then it calcified and became bone (visible on X-ray). Oh my God, this conclusively proves my theory!! I previously explained that direct trauma to the bone causes a hematoma by rupturing the blood vessels between the periosteum and the bone, lifting the periosteum and forming a subperiosteal hematoma, which then forms new bone, exactly like this case, as described literally by the scientists.
So doesn’t this perfectly match what happens in bone smashing???
Study number 8#
 reader.z-library.sk
reader.z-library.sk
On a 17-year-old football player, the ulna bone kept being exposed to direct trauma, scientists reported after a period swelling at the exact site of the injury, and they reported that the cause of this swelling is “repeated micro trauma.” You can look at the study to see the hypertrophy
Proof 9#
 pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
A person fell and injured his ankle. Scientists reported very severe bone hypertrophy at the exact site of the injury, and the reason? Subperiosteal hematoma followed by calcification into bone (they mentioned this verbatim). Oh my God, this once again agrees with my statement that direct trauma to the bone causes a subperiosteal hematoma, which then calcifies and becomes bone. Another direct piece of evidence
Proof 10#
 pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
A 35-year-old woman experienced a very severe injury to her frontal bone. After a period, X-rays showed very severe bone hypertrophy at the exact site of the injury. You can look at the study and you will see massive bone hypertrophy
Proof 11#
A 30-year-old woman directly hit her finger on a cabinet, and severe bone hypertrophy occurred at the site of the injury. This means the cause of this hypertrophy is direct trauma
Proof 12#
 pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
A Muay Thai boxer, her bone was exposed to direct micro trauma. X-rays show periosteal hypertrophy at the site exposed to the impact
Proof 13#
 reader.z-library.sk
reader.z-library.sk
If you know the sport of sumo before, you will notice that participants hit each other directly. As a result, in two cases, bone hypertrophy occurred at the site of impact (as scientists mentioned verbatim due to “repeated micro trauma”). Even with a very high fat mass protecting the bones, some force still reached the bones and caused clear hypertrophy
Proof 14#
I do not know exactly what sport this is, but the athlete repeatedly hits the bone of his foot. You can look at the image below and you will see very severe bone hypertrophy, perhaps even double the bone, especially in the fibula
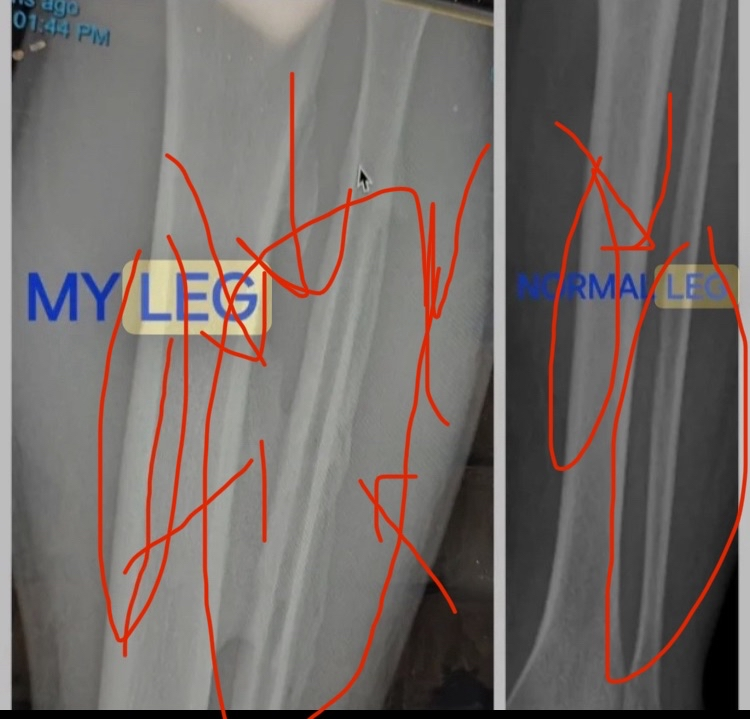
I’m done. I believe the scientific explanation and the evidence are sufficient to conclusively prove the effectiveness of bone smashing. If you want to debate or think you have a chance to win an argument against me about whether bone smashing is effective or not, you can present your argument no one is stopping you, and I will respond to it. If you start presenting stupid arguments or try to make fun of this post, I will automatically consider you a person with a very low IQ, and I will not debate you
On the other side, those who argue that it doesn’t work usually bring up weak points as well, saying that bone only increases in density, not size, and that bones need controlled, physiological types of stress to adapt, such as chewing, running, or exercising, rather than random hits.
So in the end, whether it’s the people who believe bone smashing works or those who completely dismiss it, both sides usually end up presenting weak arguments.
So thats leave the question: does bone smashing actually work
this post will divide to Tow parts
- A scientific explanation of how it works.
- Real-life scientific evidence that proves its effectiveness.
In the beginning, when a bone is struck directly, small blood vessels known as subperiosteal capillaries can rupture. Once these vessels break, blood leaks out and forms what is called a subperiosteal hematoma. This condition causes the periosteum to lift away from the cortical bone, creating an inflammatory space between the cortical bone and the periosteum.
The periosteum itself has an inner layer called the cambium, which is very rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and immature osteoblasts. Under normal conditions this layer remains relatively inactive, but it quickly becomes activated when the periosteum is lifted away from the cortex.
This elevation of the periosteum triggers an increase in the expression of Runx2, TGF-β2, and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The activation of these pathways rapidly recruits immature osteoblasts to mature into active bone-forming cells, while also driving osteoprogenitor cells to differentiate into new osteoblasts. As a result, the hematoma that formed between the periosteum and the cortex begins to calcify, leading to the formation of a new bony layer.









Sources:
-https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11786143/
-
https://sharondewitte.wordpress.com...-and-healed-periosteal-new-bone-formation.pdf
Summary: When a bone receives a direct trauam, the blood vessels rupture, leading to the formation of a subperiosteal hematoma. This lifts the periosteum, and eventually the hematoma calcifies and transforms into new bone
So after reading this, ask yourself: isn’t the swelling and bulge caused by bone smashing the clearest evidence of its effectiveness according to bone biology? Luckily, the answer is: yes.
so now i will move to part 2 :
I will show alot of studies to prove my point, so get ready please.
Study #1

Bony hypertrophy of the forearm in bareback rodeo athletes - PubMed
There are significant anatomic differences in the grip arm of bareback rodeo athletes compared to the contralateral arm. In cases of persistent pain in the grip arm and no evidence of acute injury, these differences may be relevant to pain symptoms and should be considered as part of the...
This study examined professional bareback rodeo riders (without a saddle), showing extreme bone hypertrophy in the ulna. The hypertrophy results from direct trauma and impact with the hip bone. For perspective, some individuals had up to a 92% increase in bone diameter and a 268% increase in cross-sectional area, which is extremely unusual. The image in the study shows significant hypertrophy, though not the individual with nearly doubled bone diameter.
If anyone claims this hypertrophy is caused by muscle pull alone, that is incorrect. The main reason is direct trauma to the bone, supported by the following:
- Many other sports generate high torsional forces on the bone, but hypertrophy does not exceed 10% compared to rodeo riders, indicating torsion alone cannot explain the extreme growth. Direct trauma plays a key role.
- The hypertrophy occurs only in the area where the humerus contacts the hip bone, exactly at the point of contact and impact. This localized growth confirms direct pressure and trauma are the main causes.
- Hypertrophy was observed only in riders without a saddle, where the humerus presses directly against the hip. Saddles act as a barrier that reduces direct pressure and trauma, preventing bone growth.
- The large variation in hypertrophy between individuals is due to some using protective pads that reduce trauma, while others did not. This shows how protection affects trauma and the extent of hypertrophy.
- Significant hypertrophy is seen in bareback riders, but not in saddle riders, further supporting that direct trauma and impact are the main drivers of bone growth.


[ATTACH type="full"]4165516[/ATTACH][ATTACH type="full"]4165519[/ATTACH]Study #2
https://reader.z-library.sk/read/bc...4f5ca2d25511e411cd99274aaa2a01e1e75af408e60e1
Honestly, this is personally my favorite study to prove the effectiveness of bone smashing. This study was conducted in 1980 on 60 participants, 37 of whom were professional riders without a saddle. Guess what? As I mentioned before, significant bone hypertrophy occurred only in those who practiced horseback riding without a saddle (I explained the reason before, because this type requires the rider’s ulna to hit and contact the hip). To understand more about this process that happens during the race, here is a direct quote from the study:
“On observing a contestant who is riding, the riding arm is noted to contact the anterior iliac crest and the heavily resined chaps (Fig. 3). The event requires strength, timing, balance, and courage. Ideally, the forearm should be tucked against the pelvis and chaps. Failure to maintain this position, resulting in hammering action of the forearm against pelvis and chaps.”
Oh my God, I can’t believe it, the scientists literally wrote “hammering action”! Who would believe this? Hammering movements on the bone cause severe bone hypertrophy. Wait, what does this remind you of? Yes, exactly the same thing you were trying to prove wrong, which is hammering your face. And luckily, the scientists also mentioned that bone hypertrophy occurred due to periosteal inflammation resulting from trauma to the bone. Yes, literally. You can look at the image below and you will notice severe bone hypertrophy at the place where the ulna hits the hip. Oh my God, all this hypertrophy happens in just an 8-second round!!! Just this very short time is enough to cause extreme bone growth. The answer is yes, lol





Study #3

Localized, time-dependent responses of rat cranial bone to repeated mild traumatic brain injuries - Scientific Reports
While it is well-established that bone responds dynamically to mechanical loading, the effects of mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) on cranial bone composition are unclear. We hypothesized that repeated mTBI (rmTBI) would change the microstructure of cranial bones, without gross skull...
The scientists wanted to study the effect of direct impacts on bone shape in skull bones. They designed a device to deliver a direct impact to the bone. They applied the impact only twice (just two light hits) and measured after two weeks and after ten weeks. After two weeks, there was mild bone hypertrophy, but after ten weeks, there was severe and very clear bone hypertrophy. This shows that the effects on bone hypertrophy continued to increase even after only two impacts. The study also mentioned that bone hypertrophy could occur due to trauma.

[ATTACH type="full"]4165536[/ATTACH][ATTACH type="full"]4165537[/ATTACH]Study #4

Unilateral mid-femoral periosteal newbone of varying aetiology in children. Radiographic analysis of 25 cases - PubMed
Thigh pain is a serious condition in childhood and should be promptly and thoroughly investigated. Twenty-five cases of thigh pain lasting between 1 day and 7 months with mid-femoral periosteal thickening were analysed. There were 10 patients with Ewing's sarcoma, 7 with eosinophilic granuloma...
The scientists reported that some children had increased thickness in the midshaft of the femur, and they stated that the cause of some of these cases was direct trauma to the bone.

Therefore, this is evidence that direct trauma can cause bone hypertrophy.
Study #5

Periosteal thickening as a manifestation of trauma in infancy - PubMed
This paper reports the findings in a study of the incidence of periosteal elevation in children and its possible relationship to child abuse. Two separate sets of radiographs of the skeleton of children were taken for a variety of diagnostic purposes. The suspected abuse set consisted of 59...
Once again, the scientists observed hypertrophy of the cortical bone due to direct trauma to the bone.

Study #6
Myositis ossificans circumscripta of the thigh: A pediatric case report - PMC
Circumscribed myositis ossificans is a benign process of focal heterotopic ossification of the soft tissues, occurring in young subjects, usually following trauma. We report a case of a 15-year-old patient who suffered a direct trauma to the thigh ...
A 15-year-old child experienced direct trauma to his femur (yes, the scientists literally mentioned direct trauma). You can look at the image below, where you will find severe bone hypertrophy at the site of the injury.

Org does now allow me for add more photos after this , so i will share the studies without photos , if u want to see the bone hypertrophy, click in the link
Study #6
Myositis ossificans circumscripta of the thigh: A pediatric case report - PMC
Circumscribed myositis ossificans is a benign process of focal heterotopic ossification of the soft tissues, occurring in young subjects, usually following trauma. We report a case of a 15-year-old patient who suffered a direct trauma to the thigh ...
A 15-year-old child experienced direct trauma to his femur (yes, the scientists literally mentioned direct trauma). You can look at the image below, where you will find severe bone hypertrophy at the site of the direct trauma
Study #7
Case Report: Ossified Subperiosteal Hematoma in the Humerus of a Lacrosse Player
A case report on a Lacrosse player (this sport requires direct contact with the opponent to gain possession of the ball). The player reported pain in the area left exposed “between his shoulder and elbow pads”. Because the area was exposed, it was subjected to direct trauma, which caused a subperiosteal hematoma. Then it calcified and became bone (visible on X-ray). Oh my God, this conclusively proves my theory!! I previously explained that direct trauma to the bone causes a hematoma by rupturing the blood vessels between the periosteum and the bone, lifting the periosteum and forming a subperiosteal hematoma, which then forms new bone, exactly like this case, as described literally by the scientists.
So doesn’t this perfectly match what happens in bone smashing???
Study number 8#
LITERA Reader
On a 17-year-old football player, the ulna bone kept being exposed to direct trauma, scientists reported after a period swelling at the exact site of the injury, and they reported that the cause of this swelling is “repeated micro trauma.” You can look at the study to see the hypertrophy
Proof 9#
Subperiosteal Hematoma of the Ankle - PMC
Periosteal reaction has a long list of differential diagnoses ranging from trauma, infection, metabolic disease to malignancy. The morphology of periosteal reaction shown in imaging studies helps to narrow down the list of differential diagnoses. A ...
A person fell and injured his ankle. Scientists reported very severe bone hypertrophy at the exact site of the injury, and the reason? Subperiosteal hematoma followed by calcification into bone (they mentioned this verbatim). Oh my God, this once again agrees with my statement that direct trauma to the bone causes a subperiosteal hematoma, which then calcifies and becomes bone. Another direct piece of evidence
Proof 10#
Post-Traumatic Peripheral Giant Osteoma in the Frontal Bone - PMC
Osteomas are benign, slow-growing tumors that most frequently occur in the craniomaxillofacial region. These tumors are mostly asymptomatic and are generally found incidentally. A giant osteoma is generally considered to be greater than 30 mm in ...
A 35-year-old woman experienced a very severe injury to her frontal bone. After a period, X-rays showed very severe bone hypertrophy at the exact site of the injury. You can look at the study and you will see massive bone hypertrophy
Proof 11#
A 30-year-old woman directly hit her finger on a cabinet, and severe bone hypertrophy occurred at the site of the injury. This means the cause of this hypertrophy is direct trauma
Proof 12#
Atypical Presentation of Non-Ossifying Fibroma in a Professional Muay Thai Boxer: A Case Report and a Narrative Review of the Literature - PMC
Sports injuries occur during sport athletic activities, or exercising. However, there are some lesions which are typically associated to sports, in such a demanding and physical sport like Muay Thai that no typical lesion has been detected yet. We ...
A Muay Thai boxer, her bone was exposed to direct micro trauma. X-rays show periosteal hypertrophy at the site exposed to the impact
Proof 13#
LITERA Reader
If you know the sport of sumo before, you will notice that participants hit each other directly. As a result, in two cases, bone hypertrophy occurred at the site of impact (as scientists mentioned verbatim due to “repeated micro trauma”). Even with a very high fat mass protecting the bones, some force still reached the bones and caused clear hypertrophy
Proof 14#
I do not know exactly what sport this is, but the athlete repeatedly hits the bone of his foot. You can look at the image below and you will see very severe bone hypertrophy, perhaps even double the bone, especially in the fibula

I’m done. I believe the scientific explanation and the evidence are sufficient to conclusively prove the effectiveness of bone smashing. If you want to debate or think you have a chance to win an argument against me about whether bone smashing is effective or not, you can present your argument no one is stopping you, and I will respond to it. If you start presenting stupid arguments or try to make fun of this post, I will automatically consider you a person with a very low IQ, and I will not debate you